Page 267 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 267
Printer: Yet to Come
October 28, 2014 11:15 254mm×178mm
JWST499-Cetinkunt
JWST499-c05
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS FOR MECHATRONIC SYSTEMS 253
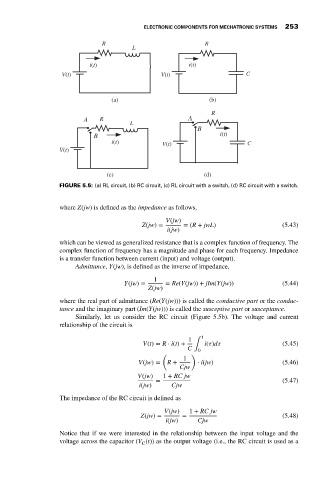
R R
L
i(t) i(t)
V(t) V(t) C
(a) (b)
R
A R A
L
B
B i(t)
i(t) V(t) C
V(t)
(c) (d)
FIGURE 5.5: (a) RL circuit, (b) RC circuit, (c) RL circuit with a switch, (d) RC circuit with a switch.
where Z(jw) is defined as the impedance as follows,
V(jw)
Z(jw) = = (R + jwL) (5.43)
i(jw)
which can be viewed as generalized resistance that is a complex function of frequency. The
complex function of frequency has a magnitude and phase for each frequency. Impedance
is a transfer function between current (input) and voltage (output).
Admittance, Y(jw), is defined as the inverse of impedance,
1
Y(jw) = = Re(Y(jw)) + jIm(Y(jw)) (5.44)
Z(jw)
where the real part of admittance (Re(Y(jw))) is called the conductive part or the conduc-
tance and the imaginary part (Im(Y(jw))) is called the susceptive part or susceptance.
Similarly, let us consider the RC circuit (Figure 5.5b). The voltage and current
relationship of the circuit is
t
1
V(t) = R ⋅ i(t) + i( )d (5.45)
C ∫ 0
( )
1
V(jw) = R + ⋅ i(jw) (5.46)
Cjw
V(jw) 1 + RC jw
= (5.47)
i(jw) Cjw
The impedance of the RC circuit is defined as
V(jw) 1 + RC jw
Z(jw) = = (5.48)
i(jw) Cjw
Notice that if we were interested in the relationship between the input voltage and the
voltage across the capacitor (V (t)) as the output voltage (i.e., the RC circuit is used as a
C