Page 314 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 314
JWST499-Cetinkunt
JWST499-c05
300 MECHATRONICS Printer: Yet to Come October 28, 2014 11:15 254mm×178mm
R
C
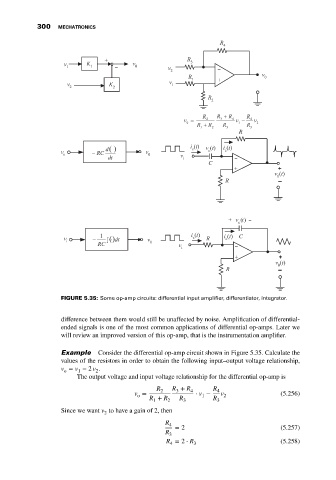
FIGURE 5.35: Some op-amp circuits: differential input amplifier, differentiator, integrator.
difference between them would still be unaffected by noise. Amplification of differential-
ended signals is one of the most common applications of differential op-amps. Later we
will review an improved version of this op-amp, that is the instrumentation amplifier.
Example Consider the differential op-amp circuit shown in Figure 5.35. Calculate the
values of the resistors in order to obtain the following input–output voltage relationship,
v = v − 2 v .
2
1
o
The output voltage and input voltage relationship for the differential op-amp is
R 2 R + R 4 R 4
3
v = ⋅ v − v (5.256)
o 1 2
R + R R R
1 2 3 3
Since we want v to have a gain of 2, then
2
R 4 = 2 (5.257)
R
3
R = 2 ⋅ R 3 (5.258)
4