Page 139 - Servo Motors and Industrial Control Theory -
P. 139
134 8 Actuators Based on Electro-Rheological Fluid
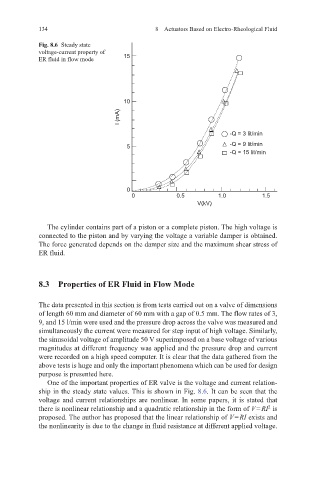
Fig. 8.6 Steady state
voltage-current property of
ER fluid in flow mode 15
10
I (mA)
-Q = 3 lit/min
5 -Q = 9 lit/min
-Q = 15 lit/min
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5
V(kV)
The cylinder contains part of a piston or a complete piston. The high voltage is
connected to the piston and by varying the voltage a variable damper is obtained.
The force generated depends on the damper size and the maximum shear stress of
ER fluid.
8.3 Properties of ER Fluid in Flow Mode
The data presented in this section is from tests carried out on a valve of dimensions
of length 60 mm and diameter of 60 mm with a gap of 0.5 mm. The flow rates of 3,
9, and 15 l/min were used and the pressure drop across the valve was measured and
simultaneously the current were measured for step input of high voltage. Similarly,
the sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 50 V superimposed on a base voltage of various
magnitudes at different frequency was applied and the pressure drop and current
were recorded on a high speed computer. It is clear that the data gathered from the
above tests is huge and only the important phenomena which can be used for design
purpose is presented here.
One of the important properties of ER valve is the voltage and current relation-
ship in the steady state values. This is shown in Fig. 8.6. It can be seen that the
voltage and current relationships are nonlinear. In some papers, it is stated that
2
there is nonlinear relationship and a quadratic relationship in the form of V = RI is
proposed. The author has proposed that the linear relationship of V = RI exists and
the nonlinearity is due to the change in fluid resistance at different applied voltage.