Page 182 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 182
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
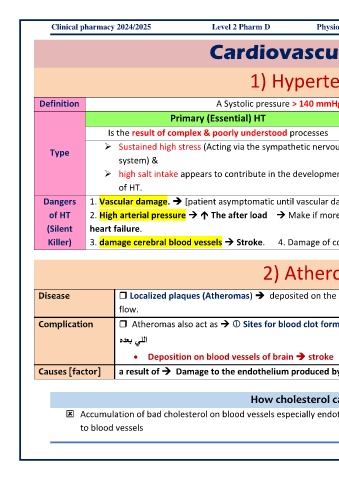
Cardiovascular diseases
1) Hypertension = HT
Definition A Systolic pressure > 140 mmHg and/or A Diastolic pressure > 80-90 mmHg.
Primary (Essential) HT Secondary HT
Is the result of complex & poorly understood processes Is a result of known disease
➢ Sustained high stress (Acting via the sympathetic nervous 1. Kidney diseases Cause HT because of high blood volume.
Type
system) & 2. Reduction of renal blood flow ↑ blood pressure by stimulating
➢ high salt intake appears to contribute in the development rennin secretion.
of HT.
Dangers 1. Vascular damage. ➔ [patient asymptomatic until vascular damage has occurred] So, HT is often referred to as (a silent killer).
of HT 2. High arterial pressure The after load Make if more difficult for the ventricles to eject blood ➔ work harder ➔ Congestive
(Silent heart failure.
Killer) 3. damage cerebral blood vessels Stroke. 4. Damage of coronary Atherosclerosis heart disease & Stroke.
2) Atherosclerosis
Disease Localized plaques (Atheromas) ➔ deposited on the lumen of the artery Make the artery stiffer & more resistant to blood
flow.
Complication Atheromas also act as Sites for blood clot formation Blood supply to an organ. ➔ may block heart ➔ Angina ➔
هدعب يللا
• Deposition on blood vessels of brain ➔ stroke
Causes [factor] a result of Damage to the endothelium produced by 1- Smoking. 2- HT 3- Blood Cholesterol. 4- Diabetes.
How cholesterol cause atherosclerosis:
Accumulation of bad cholesterol on blood vessels especially endothelium ➔ WBCs phagocyte it ➔ phagocytosis ➔ enlargement ➔ damage
to blood vessels
| P a g e 119