Page 28 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 28
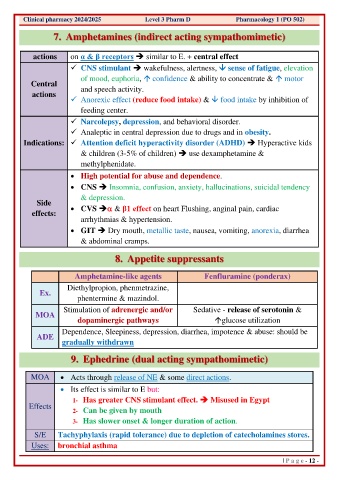
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
7. Amphetamines (indirect acting sympathomimetic)
actions on α & β receptors ➔ similar to E. + central effect
✓ CNS stimulant ➔ wakefulness, alertness, sense of fatigue, elevation
of mood, euphoria, confidence & ability to concentrate & motor
Central and speech activity.
actions
✓ Anorexic effect (reduce food intake) & food intake by inhibition of
feeding center.
✓ Narcolepsy, depression, and behavioral disorder.
✓ Analeptic in central depression due to drugs and in obesity.
Indications: ✓ Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) ➔ Hyperactive kids
& children (3-5% of children) ➔ use dexamphetamine &
methylphenidate.
• High potential for abuse and dependence.
• CNS ➔ Insomnia, confusion, anxiety, hallucinations, suicidal tendency
& depression.
Side
effects: • CVS ➔ & β1 effect on heart Flushing, anginal pain, cardiac
arrhythmias & hypertension.
• GIT ➔ Dry mouth, metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea
& abdominal cramps.
8. Appetite suppressants
Amphetamine-like agents Fenfluramine (ponderax)
Diethylpropion, phenmetrazine,
Ex.
phentermine & mazindol.
Stimulation of adrenergic and/or Sedative - release of serotonin &
MOA
dopaminergic pathways glucose utilization
Dependence, Sleepiness, depression, diarrhea, impotence & abuse: should be
ADE
gradually withdrawn
9. Ephedrine (dual acting sympathomimetic)
MOA • Acts through release of NE & some direct actions.
• Its effect is similar to E but:
1- Has greater CNS stimulant effect. ➔ Misused in Egypt
Effects
2- Can be given by mouth
3- Has slower onset & longer duration of action.
S/E Tachyphylaxis (rapid tolerance) due to depletion of catecholamines stores.
Uses: bronchial asthma
| P a g e - 12 -