Page 58 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 58
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
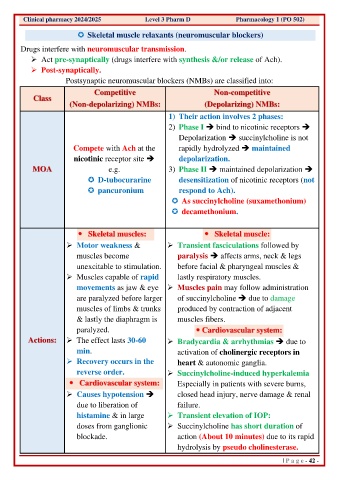
Skeletal muscle relaxants (neuromuscular blockers)
Drugs interfere with neuromuscular transmission.
➢ Act pre-synaptically (drugs interfere with synthesis &/or release of Ach).
➢ Post-synaptically.
Postsynaptic neuromuscular blockers (NMBs) are classified into:
Competitive Non-competitive
Class
(Non-depolarizing) NMBs: (Depolarizing) NMBs:
1) Their action involves 2 phases:
2) Phase I ➔ bind to nicotinic receptors ➔
Depolarization ➔ succinylcholine is not
Compete with Ach at the rapidly hydrolyzed ➔ maintained
nicotinic receptor site ➔ depolarization.
MOA e.g. 3) Phase II ➔ maintained depolarization ➔
D-tubocurarine desensitization of nicotinic receptors (not
pancuronium respond to Ach).
As succinylcholine (suxamethonium)
decamethonium.
Skeletal muscles: Skeletal muscle:
➢ Motor weakness & ➢ Transient fasciculations followed by
muscles become paralysis ➔ affects arms, neck & legs
unexcitable to stimulation. before facial & pharyngeal muscles &
➢ Muscles capable of rapid lastly respiratory muscles.
movements as jaw & eye ➢ Muscles pain may follow administration
are paralyzed before larger of succinylcholine ➔ due to damage
muscles of limbs & trunks produced by contraction of adjacent
& lastly the diaphragm is muscles fibers.
paralyzed. Cardiovascular system:
Actions: ➢ The effect lasts 30-60 ➢ Bradycardia & arrhythmias ➔ due to
min. activation of cholinergic receptors in
➢ Recovery occurs in the heart & autonomic ganglia.
reverse order. ➢ Succinylcholine-induced hyperkalemia
Cardiovascular system: Especially in patients with severe burns,
➢ Causes hypotension ➔ closed head injury, nerve damage & renal
due to liberation of failure.
histamine & in large ➢ Transient elevation of IOP:
doses from ganglionic ➢ Succinylcholine has short duration of
blockade. action (About 10 minutes) due to its rapid
hydrolysis by pseudo cholinesterase.
| P a g e - 42 -