Page 77 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 77
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
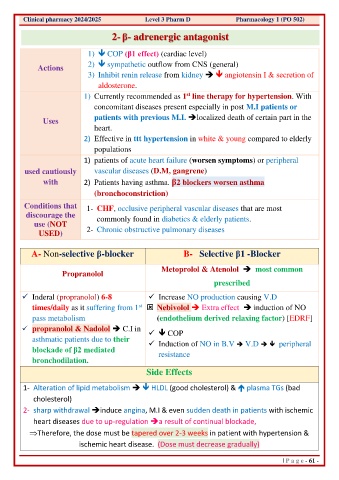
2- β- adrenergic antagonist
1) COP (β1 effect) (cardiac level)
Actions 2) sympathetic outflow from CNS (general)
3) Inhibit renin release from kidney ➔ angiotensin I & secretion of
aldosterone.
st
1) Currently recommended as 1 line therapy for hypertension. With
concomitant diseases present especially in post M.I patients or
Uses patients with previous M.I. ➔localized death of certain part in the
heart.
2) Effective in ttt hypertension in white & young compared to elderly
populations
1) patients of acute heart failure (worsen symptoms) or peripheral
used cautiously vascular diseases (D.M, gangrene)
with 2) Patients having asthma. β2 blockers worsen asthma
(bronchoconstriction)
Conditions that 1- CHF, occlusive peripheral vascular diseases that are most
discourage the commonly found in diabetics & elderly patients.
use (NOT
USED) 2- Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases
A- Non-selective β-blocker B- Selective β1 -Blocker
Metoprolol & Atenolol ➔ most common
Propranolol
prescribed
✓ Inderal (propranolol) 6-8 ✓ Increase NO production causing V.D
st
times/daily as it suffering from 1 Nebivolol ➔ Extra effect ➔ induction of NO
pass metabolism (endothelium derived relaxing factor) [EDRF]
✓ propranolol & Nadolol ➔ C.I in ✓ COP
asthmatic patients due to their ✓ Induction of NO in B.V ➔ V.D ➔ peripheral
blockade of β2 mediated resistance
bronchodilation.
Side Effects
1- Alteration of lipid metabolism ➔ HLDL (good cholesterol) & plasma TGs (bad
cholesterol)
2- sharp withdrawal ➔induce angina, M.I & even sudden death in patients with ischemic
heart diseases due to up-regulation ➔a result of continual blockade,
Therefore, the dose must be tapered over 2-3 weeks in patient with hypertension &
ischemic heart disease. (Dose must decrease gradually)
| P a g e - 61 -