Page 43 - Analytical Chemistry I E-book
P. 43
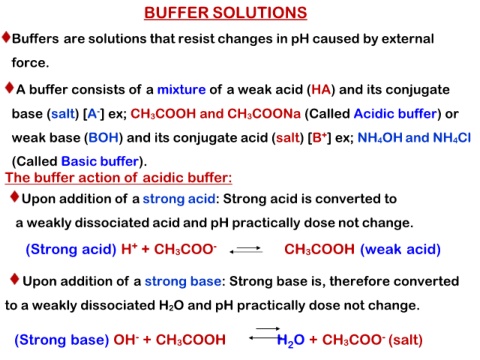
BUFFER SOLUTIONS
Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH caused by external
force.
A buffer consists of a mixture of a weak acid (HA) and its conjugate
base (salt) [A-] ex; CH3COOH and CH3COONa (Called Acidic buffer) or
weak base (BOH) and its conjugate acid (salt) [B+] ex; NH4OH and NH4Cl
(Called Basic buffer).
The buffer action of acidic buffer:
Upon addition of a strong acid: Strong acid is converted to
a weakly dissociated acid and pH practically dose not change.
(Strong acid) H+ + CH3COO- CH3COOH (weak acid)
Upon addition of a strong base: Strong base is, therefore converted
to a weakly dissociated H2O and pH practically dose not change.
(Strong base) OH- + CH3COOH H2O + CH3COO- (salt)