Page 120 - MNU-PM502- Pharmaeutical Microbiology Theoritical Book
P. 120
Pharm D- Clinical Pharmacy Program Third Level Pharmaceutical Microbiology& Antimicrobials (PM 502)
5- Inhibitors of other metabolic processes.
Sulfonamides
Sulfadiazine Sulfadimidine Sulfamethoxazole
Mechanism: Structural analogues of P- aminobenzoic acid, compete with the
Para aminobenzoic acid of the active site of dihydropteroate synthetase, an
enzyme which catalyzes the synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid.
Trimethoprim
Mechanism: is a structural analog of dihydrofolate and therefore inhibits
dihydrofolate reductase, which is required for conversion of dihydrofolate to
THF.
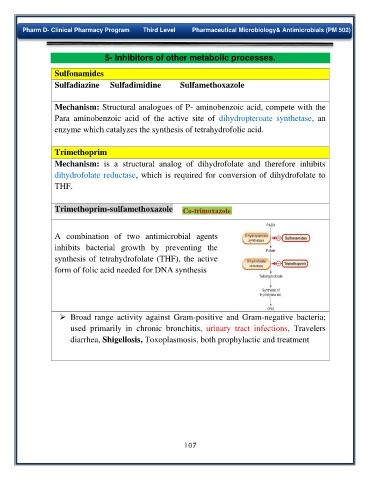
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Co-trimoxazole
A combination of two antimicrobial agents
inhibits bacterial growth by preventing the
synthesis of tetrahydrofolate (THF), the active
form of folic acid needed for DNA synthesis
➢ Broad range activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria;
used primarily in chronic bronchitis, urinary tract infections, Travelers
diarrhea, Shigellosis, Toxoplasmosis, both prophylactic and treatment
107