Page 10 - Gastrointestinal Bleeding (Xuất huyết tiêu hóa)
P. 10
284 PART III Symptoms, Signs, and Biopsychosocial Issues
blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen level, hemoglobin level, heart be given to prophylactic endotracheal intubation to minimize the
rate, syncope, melena, liver disease, and heart failure, to assess a risk of airway aspiration.
patient’s risk for needing clinical interventions to control bleed- Once the endoscope is inserted, the first thing to look for is
ing (e.g., blood transfusions, endoscopic therapy, surgery). The blood in the GI tract lumen. Examining all the nonbloody mucosa
67
Clinical Rockall Score is based on the patient’s age, shock, and quickly is often best to document that these areas are free of any
coexisting illnesses. The artificial neural network instrument uses lesions. Then, any liquid blood that can be aspirated should be
68
21 clinical variables to help predict the presence of SRH at endos- removed. Aspiration of blood can be aided by water irrigation
69
copy (see later) and the need for endoscopic therapy. AIMS65 is to dilute the blood. Other options to remove blood and clots are
an aggregate score of 5 pre-endoscopy variables (serum albumin to use an endoscope with a very large (6 mm) suction channel
<3.0 g/dL, INR >1.5, altered mental status, systolic blood pres- or to use an accessory on a therapeutic endoscope that suctions
sure ≤90 mm Hg, and age >65); an AIMS65 score less than 2 is directly through the suction port, bypassing the umbilical cord of
associated with a lower risk of mortality, length of stay, and cost of the instrument. If large clots cannot be removed with suction, the
hospitalization than a score of 2 or more. 70 patient can be turned onto his or her back or right side, provided
The most commonly used postendoscopy scoring system is that the patient is intubated to protect against aspiration. Raising
68
the Complete Rockall Score (Table 20.3). The Complete Rock- the head of the bed can also help move a clot distally from the
all Score includes the Clinical Rockall Score (pre-endoscopy gastric fundus. Any visualized adherent fresh blood or clot should
variables—patient age, shock, and coexisting illnesses) and endo- be followed to find its origin. If too much blood is present in the
scopic findings, including endoscopic SRH (see later). The Rock- stomach to allow detection of a bleeding lesion, another dose (or
all Score after endoscopic therapy correlates well with mortality an initial dose) of a prokinetic agent (e.g., erythromycin, meto-
but not as well with the risk of rebleeding. 71-73 The Rockall risk clopramide) should be considered, lavage should be repeated with
stratification schemes can also be used to identify patients at low a large orogastric tube, or the examination should be repeated in
risk for poor outcomes (i.e., Rockall Scores of 0 to 2) who should the next 24 hours if the patient has stabilized. If bleeding from the
be considered for early discharge from the hospital. 74 duodenum is suspected but not identified with a forward-viewing
Other scoring systems to predict outcomes from UGI bleed- endoscope, a side-viewing duodenoscope should be used to exam-
ing after endoscopy include the Baylor Scoring System and the ine the duodenal wall and ampulla.
Cedars-Sinai Bleeding Index. 75-78 In general, all of these scoring
79
systems are better at determining mortality than rebleeding. Peptic Ulcer
Upper Endoscopic Technique In the past, peptic ulcer, most commonly gastric or duodenal
ulcer, accounted for 50% of UGI bleeds and approximately
A therapeutic endoscope facilitates aspiration of blood and the use 100,000 hospitalizations/year in the US. 80,81 Some data have
of large accessories. Target jet water irrigation with a foot pump suggested that the incidence of bleeding peptic ulcer decreased
through a separate small channel should be available. Patients between 1993 and 2002, whereas the proportion of ulcers caused
82
should be hemodynamically resuscitated medically prior to EGD by NSAIDs increased. Other data, however, found no change
(see earlier), and, if active bleeding is severe, consideration should in overall rates of bleeding ulcers between 1990 and 2000, but
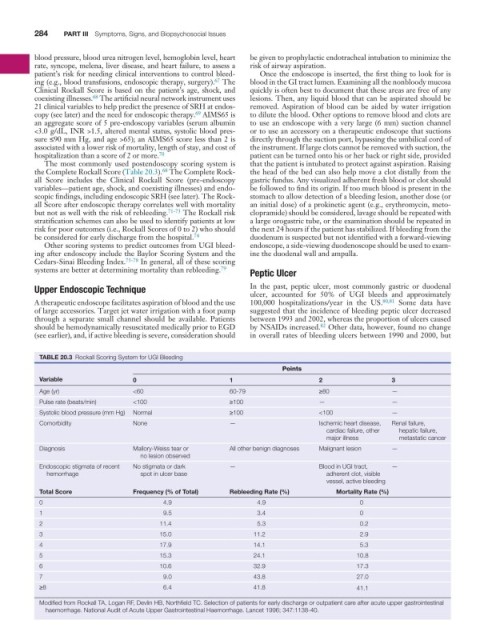
TABLE 20.3 Rockall Scoring System for UGI Bleeding
Points
Variable 0 1 2 3
Age (yr) <60 60-79 ≥80 —
Pulse rate (beats/min) <100 ≥100 — —
Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Normal ≥100 <100 —
Comorbidity None — Ischemic heart disease, Renal failure,
cardiac failure, other hepatic failure,
major illness metastatic cancer
Diagnosis Mallory-Weiss tear or All other benign diagnoses Malignant lesion —
no lesion observed
Endoscopic stigmata of recent No stigmata or dark — Blood in UGI tract, —
hemorrhage spot in ulcer base adherent clot, visible
vessel, active bleeding
Total Score Frequency (% of Total) Rebleeding Rate (%) Mortality Rate (%)
0 4.9 4.9 0
1 9.5 3.4 0
2 11.4 5.3 0.2
3 15.0 11.2 2.9
4 17.9 14.1 5.3
5 15.3 24.1 10.8
6 10.6 32.9 17.3
7 9.0 43.8 27.0
≥8 6.4 41.8 41.1
Modified from Rockall TA, Logan RF, Devlin HB, Northfield TC. Selection of patients for early discharge or outpatient care after acute upper gastrointestinal
haemorrhage. National Audit of Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Haemorrhage. Lancet 1996; 347:1138-40.