Page 20 - Acute Pancreatitis (Viêm tụy cấp)
P. 20
CHAPTER 58 Acute Pancreatitis 911
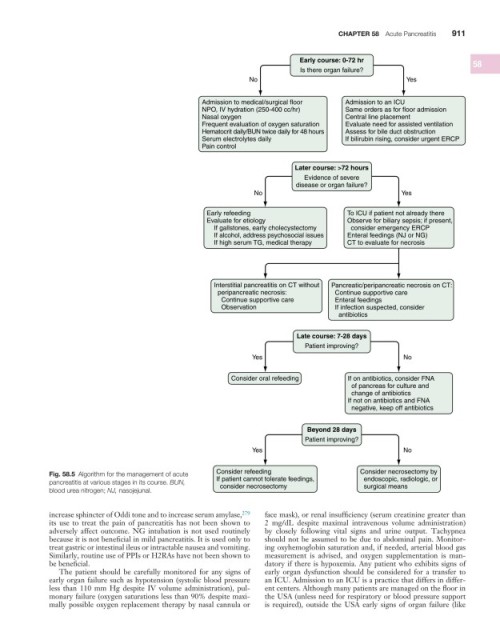
Early course: 0-72 hr 58
Is there organ failure?
No Yes
Admission to medical/surgical floor Admission to an ICU
NPO, IV hydration (250-400 cc/hr) Same orders as for floor admission
Nasal oxygen Central line placement
Frequent evaluation of oxygen saturation Evaluate need for assisted ventilation
Hematocrit daily/BUN twice daily for 48 hours Assess for bile duct obstruction
Serum electrolytes daily If bilirubin rising, consider urgent ERCP
Pain control
Later course: >72 hours
Evidence of severe
disease or organ failure?
No Yes
Early refeeding To ICU if patient not already there
Evaluate for etiology Observe for biliary sepsis; if present,
If gallstones, early cholecystectomy consider emergency ERCP
If alcohol, address psychosocial issues Enteral feedings (NJ or NG)
If high serum TG, medical therapy CT to evaluate for necrosis
Interstitial pancreatitis on CT without Pancreatic/peripancreatic necrosis on CT:
peripancreatic necrosis: Continue supportive care
Continue supportive care Enteral feedings
Observation If infection suspected, consider
antibiotics
Late course: 7-28 days
Patient improving?
Yes No
Consider oral refeeding If on antibiotics, consider FNA
of pancreas for culture and
change of antibiotics
If not on antibiotics and FNA
negative, keep off antibiotics
Beyond 28 days
Patient improving?
Yes No
Fig. 58.5 Algorithm for the management of acute Consider refeeding Consider necrosectomy by
pancreatitis at various stages in its course. BUN, If patient cannot tolerate feedings, endoscopic, radiologic, or
consider necrosectomy
surgical means
blood urea nitrogen; NJ, nasojejunal.
increase sphincter of Oddi tone and to increase serum amylase, 279 face mask), or renal insufficiency (serum creatinine greater than
its use to treat the pain of pancreatitis has not been shown to 2 mg/dL despite maximal intravenous volume administration)
adversely affect outcome. NG intubation is not used routinely by closely following vital signs and urine output. Tachypnea
because it is not beneficial in mild pancreatitis. It is used only to should not be assumed to be due to abdominal pain. Monitor-
treat gastric or intestinal ileus or intractable nausea and vomiting. ing oxyhemoglobin saturation and, if needed, arterial blood gas
Similarly, routine use of PPIs or H2RAs have not been shown to measurement is advised, and oxygen supplementation is man-
be beneficial. datory if there is hypoxemia. Any patient who exhibits signs of
The patient should be carefully monitored for any signs of early organ dysfunction should be considered for a transfer to
early organ failure such as hypotension (systolic blood pressure an ICU. Admission to an ICU is a practice that differs in differ-
less than 110 mm Hg despite IV volume administration), pul- ent centers. Although many patients are managed on the floor in
monary failure (oxygen saturations less than 90% despite maxi- the USA (unless need for respiratory or blood pressure support
mally possible oxygen replacement therapy by nasal cannula or is required), outside the USA early signs of organ failure (like