Page 52 - The Miracle in the Cell
P. 52
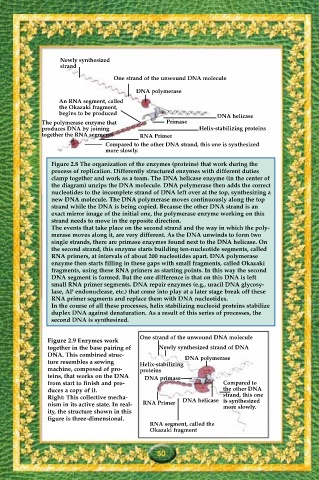
Newly synthesized
strand
One strand of the unwound DNA molecule
DNA polymerase
An RNA segment, called
the Okazaki fragment,
begins to be produced
DNA helicase
The polymerase enzyme that Primase
produces DNA by joining Helix-stabilizing proteins
together the RNA segments RNA Primer
Compared to the other DNA strand, this one is synthesized
more slowly.
Figure 2.8 The organization of the enzymes (proteins) that work during the
process of replication. Differently structured enzymes with different duties
clamp together and work as a team. The DNA helicase enzyme (in the center of
the diagram) unzips the DNA molecule. DNA polymerase then adds the correct
nucleotides to the incomplete strand of DNA left over at the top, synthesizing a
new DNA molecule. The DNA polymerase moves continuously along the top
strand while the DNA is being copied. Because the other DNA strand is an
exact mirror image of the initial one, the polymerase enzyme working on this
strand needs to move in the opposite direction.
The events that take place on the second strand and the way in which the poly-
merase moves along it, are very different. As the DNA unwinds to form two
single strands, there are primase enzymes found next to the DNA helicase. On
the second strand, this enzyme starts building ten-nucleotide segments, called
RNA primers, at intervals of about 200 nucleotides apart. DNA polymerase
enzyme then starts filling in these gaps with small fragments, called Okazaki
fragments, using these RNA primers as starting points. In this way the second
DNA segment is formed. But the one difference is that on this DNA is left
small RNA primer segments. DNA repair enzymes (e.g., uracil DNA glycosy-
lase, AP endonuclease, etc.) that come into play at a later stage break off these
RNA primer segments and replace them with DNA nucleotides.
In the course of all these processes, helix stabilizing nucleoid proteins stabilize
duplex DNA against denaturation. As a result of this series of processes, the
second DNA is synthesized.
One strand of the unwound DNA molecule
Figure 2.9 Enzymes work
together in the base pairing of Newly synthesized strand of DNA
DNA. This combined struc- DNA polymerase
ture resembles a sewing
Helix-stabilizing
machine, composed of pro- proteins
teins, that works on the DNA DNA primase
from start to finish and pro- Compared to
duces a copy of it. the other DNA
strand, this one
Right: This collective mecha- DNA helicase is synthesized
nism in its active state. In real- RNA Primer more slowly.
ity, the structure shown in this
figure is three-dimensional.
RNA segment, called the
Okazaki fragment
50