Page 67 - Practical Handout bio 2 mnu 2025_Neat
P. 67
Level two – Semester 4 - PharmD Biochemistry-II PB-403 (Practical course) 2024/2025
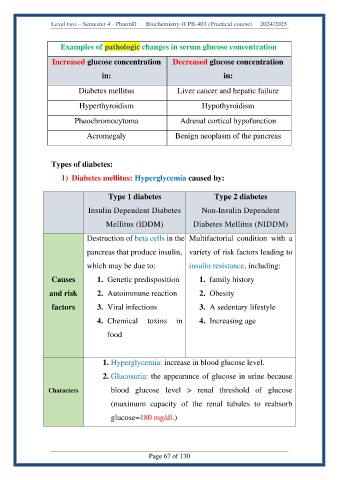
Examples of pathologic changes in serum glucose concentration
Increased glucose concentration Decreased glucose concentration
in: in:
Diabetes mellitus Liver cancer and hepatic failure
Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism
Pheochromocytoma Adrenal cortical hypofunction
Acromegaly Benign neoplasm of the pancreas
Types of diabetes:
1) Diabetes mellitus: Hyperglycemia caused by:
Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes
Insulin Dependent Diabetes Non-Insulin Dependent
Mellitus (IDDM) Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)
Destruction of beta cells in the Multifactorial condition with a
pancreas that produce insulin, variety of risk factors leading to
which may be due to: insulin resistance, including:
Causes 1. Genetic predisposition 1. family history
and risk 2. Autoimmune reaction 2. Obesity
factors 3. Viral infections 3. A sedentary lifestyle
4. Chemical toxins in 4. Increasing age
food
1. Hyperglycemia: increase in blood glucose level.
2. Glucosuria: the appearance of glucose in urine because
Characters blood glucose level > renal threshold of glucose
(maximum capacity of the renal tubules to reabsorb
glucose=180 mg/dl.)
Page 67 of 130