Page 20 - Doc1
P. 20
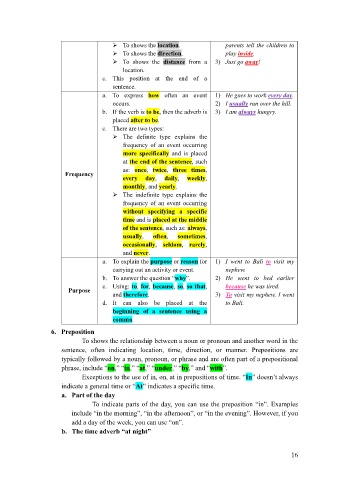
➢ To shows the location. parents tell the children to
➢ To shows the direction. play inside.
➢ To shows the distance from a 3) Just go away!
location.
c. This position at the end of a
sentence.
a. To express how often an event 1) He goes to work every day.
occurs. 2) I usually run over the hill.
b. If the verb is to be, then the adverb is 3) I am always hungry.
placed after to be.
c. There are two types:
➢ The definite type explains the
frequency of an event occurring
more specifically and is placed
at the end of the sentence, such
as: once, twice, three times,
Frequency
every day, daily, weekly,
monthly, and yearly.
➢ The indefinite type explains the
frequency of an event occurring
without specifying a specific
time and is placed at the middle
of the sentence, such as: always,
usually, often, sometimes,
occasionally, seldom, rarely,
and never.
a. To explain the purpose or reason for 1) I went to Bali to visit my
carrying out an activity or event. nephew.
b. To answer the question “why”. 2) He went to bed earlier
c. Using: to, for, because, so, so that, because he was tired.
Purpose
and therefore. 3) To visit my nephew, I went
d. It can also be placed at the to Bali.
beginning of a sentence using a
comma.
6. Preposition
To shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the
sentence, often indicating location, time, direction, or manner. Prepositions are
typically followed by a noun, pronoun, or phrase and are often part of a prepositional
phrase, include “on,” “in,” “at,” “under,” “by,” and “with”.
Exceptions to the use of in, on, at in prepositions of time. “In” doesn’t always
indicate a general time or “At” indicates a specific time.
a. Part of the day
To indicate parts of the day, you can use the preposition “in”. Examples
include “in the morning”, “in the afternoon”, or “in the evening”. However, if you
add a day of the week, you can use “on”.
b. The time adverb “at night”
16