Page 16 - Doc1
P. 16
when you came to pick me up. competition.
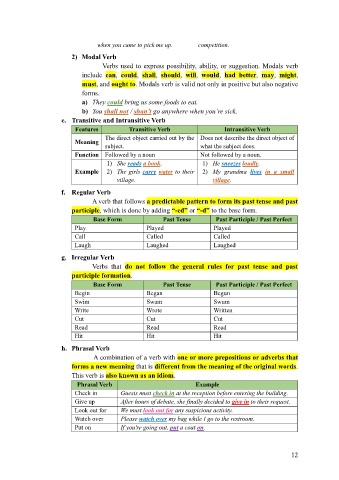
2) Modal Verb
Verbs used to express possibility, ability, or suggestion. Modals verb
include can, could, shall, should, will, would, had better, may, might,
must, and ought to. Modals verb is valid not only in positive but also negative
forms.
a) They could bring us some foods to eat.
b) You shall not / shan’t go anywhere when you’re sick.
e. Transitive and Intransitive Verb
Features Transitive Verb Intransitive Verb
The direct object carried out by the Does not describe the direct object of
Meaning
subject. what the subject does.
Function Followed by a noun Not followed by a noun.
1) She reads a book. 1) He sneezes loudly.
Example 2) The girls carry water to their 2) My grandma lives in a small
village. village.
f. Regular Verb
A verb that follows a predictable pattern to form its past tense and past
participle, which is done by adding “-ed” or “-d” to the base form.
Base Form Past Tense Past Participle / Past Perfect
Play Played Played
Call Called Called
Laugh Laughed Laughed
g. Irregular Verb
Verbs that do not follow the general rules for past tense and past
participle formation.
Base Form Past Tense Past Participle / Past Perfect
Begin Began Begun
Swim Swam Swum
Write Wrote Written
Cut Cut Cut
Read Read Read
Hit Hit Hit
h. Phrasal Verb
A combination of a verb with one or more prepositions or adverbs that
forms a new meaning that is different from the meaning of the original words.
This verb is also known as an idiom.
Phrasal Verb Example
Check in Guests must check in at the reception before entering the building.
Give up After hours of debate, she finally decided to give in to their request.
Look out for We must look out for any suspicious activity.
Watch over Please watch over my bag while I go to the restroom.
Put on If you're going out, put a coat on.
12