Page 18 - Doc1
P. 18
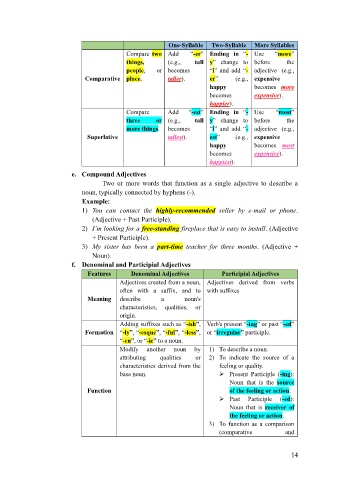
One-Syllable Two-Syllable More Syllables
Compare two Add “-er” Ending in “- Use “more”
things, (e.g., tall y” change to before the
people, or becomes “i” and add “- adjective (e.g.,
Comparative place. taller). er” (e.g., expensive
happy becomes more
becomes expensive).
happier).
Compare Add “-est” Ending in “- Use “most”
three or (e.g., tall y” change to before the
more things. becomes “i” and add “- adjective (e.g.,
Superlative tallest). est” (e.g., expensive
happy becomes most
becomes expensive).
happiest).
e. Compound Adjectives
Two or more words that function as a single adjective to describe a
noun, typically connected by hyphens (-).
Example:
1) You can contact the highly-recommended seller by e-mail or phone.
(Adjective + Past Participle).
2) I’m looking for a free-standing fireplace that is easy to install. (Adjective
+ Present Participle).
3) My sister has been a part-time teacher for three months. (Adjective +
Noun).
f. Denominal and Participial Adjectives
Features Denominal Adjectives Participial Adjectives
Adjectives created from a noun, Adjectives derived from verbs
often with a suffix, and to with suffixes
Meaning describe a noun's
characteristics, qualities, or
origin.
Adding suffixes such as “-ish”, Verb's present “-ing” or past “-ed”
Formation “-ly”, “-esque”, “-ful”, “-less”, or “irregular” participle.
“-en”, or “-ic” to a noun.
Modify another noun by 1) To describe a noun.
attributing qualities or 2) To indicate the source of a
characteristics derived from the feeling or quality.
base noun. ➢ Present Participle (-ing):
Noun that is the source
Function of the feeling or action.
➢ Past Participle (-ed):
Noun that is receiver of
the feeling or action.
3) To function as a comparison
(comparative and
14