Page 26 - Doc1
P. 26
CHAPTER VI
MODALS
A. Definition of Modals
A modal verb is a type of auxiliary verb that adds meaning to another verb,
expressing concepts like possibility, ability, permission, or obligation. Common modal
verbs include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would.
For example:
You must leave.
The modal verb must indicate a necessity or obligation.
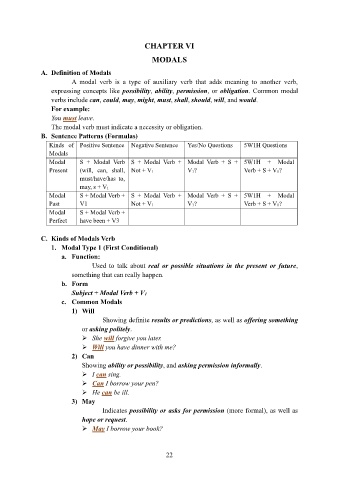
B. Sentence Patterns (Formulas)
Kinds of Positive Sentence Negative Sentence Yes/No Questions 5W1H Questions
Modals
Modal S + Modal Verb S + Modal Verb + Modal Verb + S + 5W1H + Modal
Present (will, can, shall, Not + V1 V1? Verb + S + V1?
must/have/has to,
may, s + V1
Modal S + Modal Verb + S + Modal Verb + Modal Verb + S + 5W1H + Modal
Past V1 Not + V1 V1? Verb + S + V1?
Modal S + Modal Verb +
Perfect have been + V3
C. Kinds of Modals Verb
1. Modal Type 1 (First Conditional)
a. Function:
Used to talk about real or possible situations in the present or future,
something that can really happen.
b. Form
Subject + Modal Verb + V1
c. Common Modals
1) Will
Showing definite results or predictions, as well as offering something
or asking politely.
➢ She will forgive you later.
➢ Will you have dinner with me?
2) Can
Showing ability or possibility, and asking permission informally.
➢ I can sing.
➢ Can I borrow your pen?
➢ He can be ill.
3) May
Indicates possibility or asks for permission (more formal), as well as
hope or request.
➢ May I borrow your book?
22