Page 27 - Doc1
P. 27
➢ May you both full of happiness.
4) Shall
Shows an offer or promise (more formal, usually with “I” or “We”).
➢ Shall I turn on the light?
➢ I shall meet her tomorrow.
5) Must or Have/Has to
Shows a real obligation in the future. Use need not or needn't instead
of must not or mustn't for the negative form of must or for expressions to
answer questions in an interrogative sentence. Indicates a prohibition or
something that is not allowed with must not/mustn't.
➢ You must go now.
➢ Must I go now? Yes, you must or Yes, you need.
➢ You must not smoke in the class.
➢ You must read this book / You have to read this book.
6) Should or Ought to
Indicates advice or a small possibility in the future (real possibility
but not certain). Work or tasks that are not fulfilled, not completed or
neglected, especially from the specified time limit.
➢ She ought to submit the assignment punctually.
➢ You should study harder.
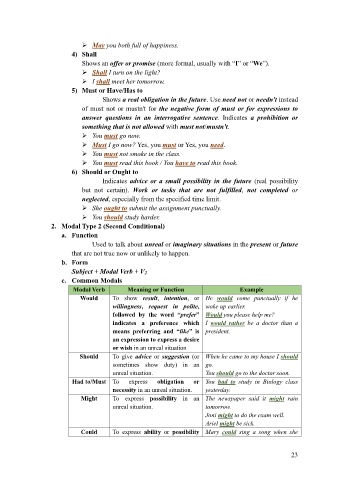
2. Modal Type 2 (Second Conditional)
a. Function
Used to talk about unreal or imaginary situations in the present or future
that are not true now or unlikely to happen.
b. Form
Subject + Modal Verb + V2
c. Common Modals
Modal Verb Meaning or Function Example
Would To show result, intention, or He would come punctually if he
willingness, request in polite, woke up earlier.
followed by the word “prefer” Would you please help me?
indicates a preference which I would rather be a doctor than a
means preferring and “like” is president.
an expression to express a desire
or wish in an unreal situation
Should To give advice or suggestion (or When he came to my house I should
sometimes show duty) in an go.
unreal situation. You should go to the doctor soon.
Had to/Must To express obligation or You had to study in Biology class
necessity in an unreal situation. yesterday.
Might To express possibility in an The newspaper said it might rain
unreal situation. tomorrow.
Joni might to do the exam well.
Ariel might be sick.
Could To express ability or possibility Mary could sing a song when she
23