Page 120 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 120
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
Factors affecting solubility of precipitate
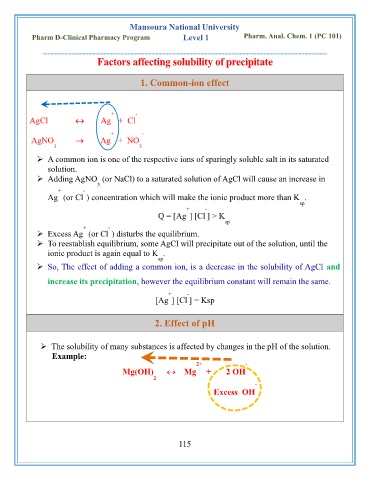
1. Common-ion effect
+ -
AgCl Ag + Cl
+ -
AgNO → Ag + NO
3 3
➢ A common ion is one of the respective ions of sparingly soluble salt in its saturated
solution.
➢ Adding AgNO (or NaCl) to a saturated solution of AgCl will cause an increase in
3
+ -
Ag (or Cl ) concentration which will make the ionic product more than K .
sp
+ -
Q = [Ag ] [Cl ] > K
sp
+ -
➢ Excess Ag (or Cl ) disturbs the equilibrium.
➢ To reestablish equilibrium, some AgCl will precipitate out of the solution, until the
ionic product is again equal to K .
sp
➢ So, The effect of adding a common ion, is a decrease in the solubility of AgCl and
increase its precipitation, however the equilibrium constant will remain the same.
+ -
[Ag ] [Cl ] = Ksp
2. Effect of pH
➢ The solubility of many substances is affected by changes in the pH of the solution.
Example:
2+ -
Mg(OH) Mg + 2 OH
2
-
Excess OH
115