Page 121 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 121
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
-
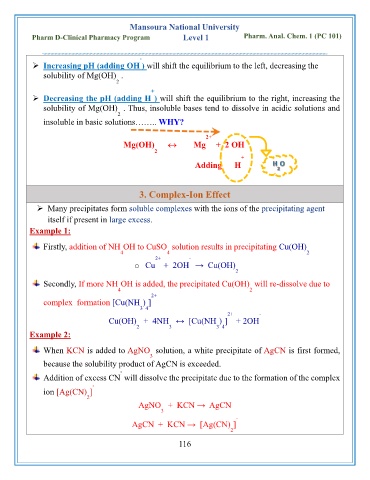
➢ Increasing pH (adding OH ) will shift the equilibrium to the left, decreasing the
solubility of Mg(OH) .
2
+
➢ Decreasing the pH (adding H ) will shift the equilibrium to the right, increasing the
solubility of Mg(OH) . Thus, insoluble bases tend to dissolve in acidic solutions and
2
insoluble in basic solutions…….. WHY?
2+ -
Mg(OH) Mg + 2 OH
2
+
Adding H
3. Complex-Ion Effect
➢ Many precipitates form soluble complexes with the ions of the precipitating agent
itself if present in large excess.
Example 1:
Firstly, addition of NH OH to CuSO solution results in precipitating Cu(OH)
4 4 2
2+ -
o Cu + 2OH → Cu(OH)
2
Secondly, If more NH OH is added, the precipitated Cu(OH) will re-dissolve due to
4 2
2+
complex formation [Cu(NH ) ]
3 4
2+ -
Cu(OH) + 4NH ↔ [Cu(NH ) ] + 2OH
2 3 3 4
Example 2:
When KCN is added to AgNO solution, a white precipitate of AgCN is first formed,
3
because the solubility product of AgCN is exceeded.
-
Addition of excess CN will dissolve the precipitate due to the formation of the complex
-
ion [Ag(CN) ]
2
AgNO + KCN → AgCN
3
-
AgCN + KCN → [Ag(CN) ]
2
116