Page 51 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 51
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
➢ Titration of the sample with the prepared standard solution and
2nd Step
observation of the E.P.
3rd Step ➢ Calculation of the sample concentration (refer to practical course).
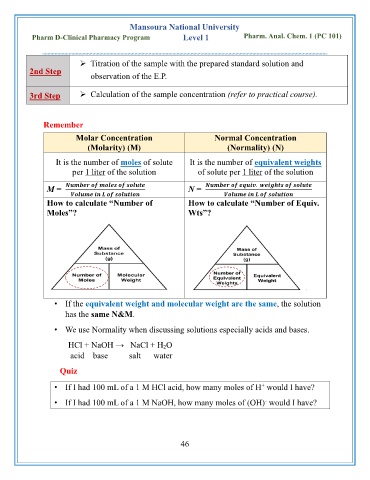
Remember
Molar Concentration Normal Concentration
(Molarity) (M) (Normality) (N)
It is the number of moles of solute It is the number of equivalent weights
per 1 liter of the solution of solute per 1 liter of the solution
M = N = .
How to calculate “Number of How to calculate “Number of Equiv.
Moles”? Wts”?
• If the equivalent weight and molecular weight are the same, the solution
has the same N&M.
• We use Normality when discussing solutions especially acids and bases.
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H 2O
acid base salt water
Quiz
+
• If I had 100 mL of a 1 M HCl acid, how many moles of H would I have?
-
• If I had 100 mL of a 1 M NaOH, how many moles of (OH) would I have?
46