Page 53 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 53
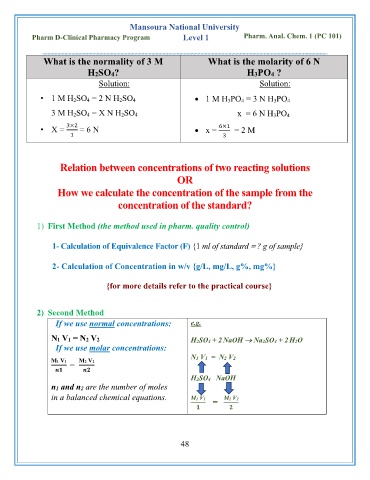
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
What is the normality of 3 M What is the molarity of 6 N
H2SO4? H3PO4 ?
Solution: Solution:
• 1 M H 2SO 4 = 2 N H 2SO 4 • 1 M H 3PO 4 = 3 N H 3PO 4
3 M H 2SO 4 = X N H 2SO 4 x = 6 N H 3PO 4
• X = 3×2 = 6 N • x = 6×1 = 2 M
1 3
Relation between concentrations of two reacting solutions
OR
How we calculate the concentration of the sample from the
concentration of the standard?
1) First Method (the method used in pharm. quality control)
1- Calculation of Equivalence Factor (F) {1 ml of standard
? g of sample}
2- Calculation of Concentration in w/v {g/L, mg/L, g%, mg%}
{for more details refer to the practical course}
2) Second Method
If we use normal concentrations: e.g.
N1 V1 = N2 V2 H2SO4 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O
If we use molar concentrations:
N1 V1 = N2 V2
M1 V1 M2 V2
=
H2SO4 NaOH
n1 and n2 are the number of moles
in a balanced chemical equations. M1 V1 = M2 V2
48