Page 54 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 54
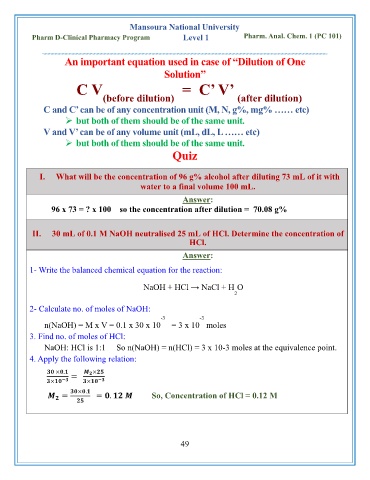
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
An important equation used in case of “Dilution of One
Solution”
C V = C’ V’
(before dilution) (after dilution)
C and C’ can be of any concentration unit (M, N, g%, mg% …… etc)
➢ but both of them should be of the same unit.
V and V’ can be of any volume unit (mL, dL, L …… etc)
➢ but both of them should be of the same unit.
Quiz
I. What will be the concentration of 96 g% alcohol after diluting 73 mL of it with
water to a final volume 100 mL.
Answer:
96 x 73 = ? x 100 so the concentration after dilution = 70.08 g%
II. 30 mL of 0.1 M NaOH neutralised 25 mL of HCl. Determine the concentration of
HCl.
Answer:
1- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H O
2
2- Calculate no. of moles of NaOH:
-3 -3
n(NaOH) = M x V = 0.1 x 30 x 10 = 3 x 10 moles
3. Find no. of moles of HCl:
NaOH: HCl is 1:1 So n(NaOH) = n(HCl) = 3 x 10-3 moles at the equivalence point.
4. Apply the following relation:
× . = ×
× − × −
× .
= = . So, Concentration of HCl = 0.12 M
49