Page 83 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 83
In contrast, the curve shown in panel (b) of Figure A.5 is U-shaped: it has a slope
that changes from negative to positive. At x equal to 50, the curve reaches its lowest
point—the smallest value of y along the curve. This point is called the minimum of the
curve. Various important curves in economics, such as the curve that represents how a
firm’s cost per unit changes as output increases, are U–shaped like this one.
Calculating the Area Below or Above a Curve Section I Basic Economic Concepts
Sometimes it is useful to be able to measure the size of the area below or above a curve.
To keep things simple, we’ll only calculate the area below or above a linear curve.
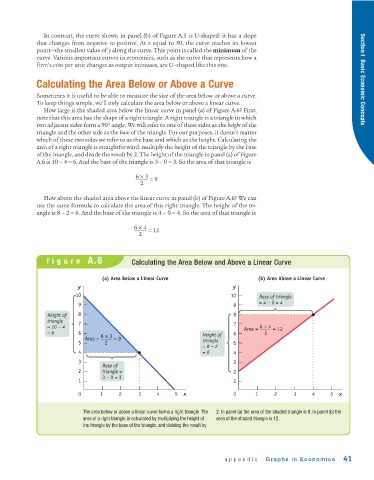
How large is the shaded area below the linear curve in panel (a) of Figure A.6? First,
note that this area has the shape of a right triangle. A right triangle is a triangle in which
two adjacent sides form a 90° angle. We will refer to one of these sides as the height of the
triangle and the other side as the base of the triangle. For our purposes, it doesn’t matter
which of these two sides we refer to as the base and which as the height. Calculating the
area of a right triangle is straightforward: multiply the height of the triangle by the base
of the triangle, and divide the result by 2. The height of the triangle in panel (a) of Figure
A.6 is 10 − 4 = 6. And the base of the triangle is 3 − 0 = 3. So the area of that triangle is
6 × 3 = 9
2
How about the shaded area above the linear curve in panel (b) of Figure A.6? We can
use the same formula to calculate the area of this right triangle. The height of the tri-
angle is 8 − 2 = 6. And the base of the triangle is 4 − 0 = 4. So the area of that triangle is
6 × 4 = 12
2
figure A.6 Calculating the Area Below and Above a Linear Curve
(a) Area Below a Linear Curve (b) Area Above a Linear Curve
y y
10 10 Base of triangle
9 9 = 4 – 0 = 4
Height of 8 8
triangle 7 7
= 10 – 4 Area = 6 × 4 = 12
= 6 6 6 × 3 Height of 6 2
Area = = 9
5 2 triangle 5
= 8 – 2
4 = 6 4
3 3
Base of
2 triangle = 2
3 – 0 = 3
1 1
0 1 2 3 4 5 x 0 1 2 3 4 5 x
The area below or above a linear curve forms a right triangle. The 2. In panel (a) the area of the shaded triangle is 9. In panel (b) the
area of a right triangle is calculated by multiplying the height of area of the shaded triangle is 12.
the triangle by the base of the triangle, and dividing the result by
appendix Graphs in Economics 41