Page 833 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 833
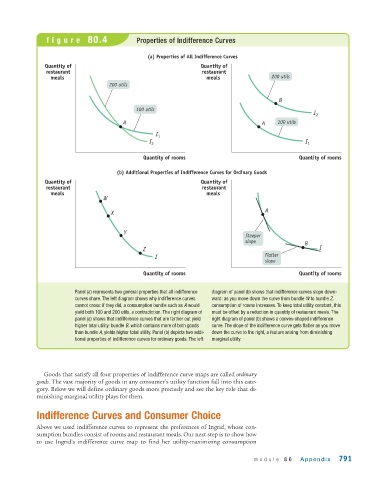
figure 80.4 Properties of Indifference Curves
(a) Properties of All Indifference Curves
Quantity of Quantity of
restaurant restaurant
meals meals 200 utils
200 utils
B
100 utils
I 2
A A 100 utils
I 1
I 2 I 1
Quantity of rooms Quantity of rooms
(b) Additional Properties of Indifference Curves for Ordinary Goods
Quantity of Quantity of
restaurant restaurant
meals meals
W
A
X
Y
Steeper
slope B
Z I
I Flatter
slope
Quantity of rooms Quantity of rooms
Panel (a) represents two general properties that all indifference diagram of panel (b) shows that indifference curves slope down-
curves share. The left diagram shows why indifference curves ward: as you move down the curve from bundle W to bundle Z,
cannot cross: if they did, a consumption bundle such as A would consumption of rooms increases. To keep total utility constant, this
yield both 100 and 200 utils, a contradiction. The right diagram of must be offset by a reduction in quantity of restaurant meals. The
panel (a) shows that indifference curves that are farther out yield right diagram of panel (b) shows a convex-shaped indifference
higher total utility: bundle B, which contains more of both goods curve. The slope of the indifference curve gets flatter as you move
than bundle A, yields higher total utility. Panel (b) depicts two addi- down the curve to the right, a feature arising from diminishing
tional properties of indifference curves for ordinary goods. The left marginal utility.
Goods that satisfy all four properties of indifference curve maps are called ordinary
goods. The vast majority of goods in any consumer’s utility function fall into this cate-
gory. Below we will define ordinary goods more precisely and see the key role that di-
minishing marginal utility plays for them.
Indifference Curves and Consumer Choice
Above we used indifference curves to represent the preferences of Ingrid, whose con-
sumption bundles consist of rooms and restaurant meals. Our next step is to show how
to use Ingrid’s indifference curve map to find her utility-maximizing consumption
module 80 Appendix 791