Page 280 - NGTU_paper_withoutVideo
P. 280
Modern Geomatics Technologies and Applications
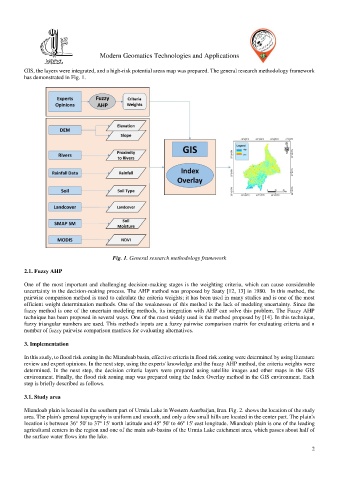
GIS, the layers were integrated, and a high-risk potential areas map was prepared. The general research methodology framework
has demonstrated in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. General research methodology framework
2.1. Fuzzy AHP
One of the most important and challenging decision-making stages is the weighting criteria, which can cause considerable
uncertainty in the decision-making process. The AHP method was proposed by Saaty [12, 13] in 1980. In this method, the
pairwise comparison method is used to calculate the criteria weights; it has been used in many studies and is one of the most
efficient weight determination methods. One of the weaknesses of this method is the lack of modeling uncertainty. Since the
fuzzy method is one of the uncertain modeling methods, its integration with AHP can solve this problem. The Fuzzy AHP
technique has been proposed in several ways. One of the most widely used is the method proposed by [14]. In this technique,
fuzzy triangular numbers are used. This method's inputs are a fuzzy pairwise comparison matrix for evaluating criteria and n
number of fuzzy pairwise comparison matrices for evaluating alternatives.
3. Implementation
In this study, to flood risk zoning in the Miandoab basin, effective criteria in flood risk zoning were determined by using literature
review and expert opinions. In the next step, using the experts' knowledge and the fuzzy AHP method, the criteria weights were
determined. In the next step, the decision criteria layers were prepared using satellite images and other maps in the GIS
environment. Finally, the flood risk zoning map was prepared using the Index Overlay method in the GIS environment. Each
step is briefly described as follows.
3.1. Study area
Miandoab plain is located in the southern part of Urmia Lake in Western Azerbaijan, Iran. Fig. 2. shows the location of the study
area. The plain's general topography is uniform and smooth, and only a few small hills are located in the center part. The plain's
location is between 36° 50' to 37º 15' north latitude and 45º 50' to 46º 15' east longitude. Miandoab plain is one of the leading
agricultural centers in the region and one of the main sub-basins of the Urmia Lake catchment area, which passes about half of
the surface water flows into the lake.
2