Page 30 - NGTU_paper_withoutVideo
P. 30
Modern Geomatics Technologies and Applications
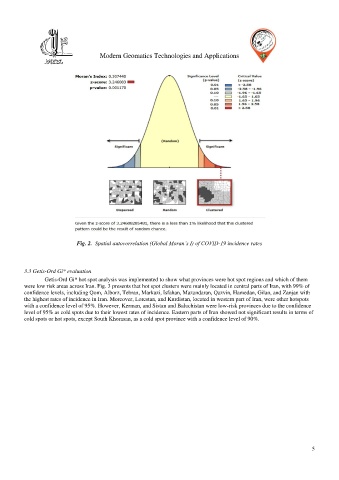
Fig. 2. Spatial autocorrelation (Global Moran’s I) of COVID-19 incidence rates
3.3 Getis-Ord Gi* evaluation
Getis-Ord Gi* hot spot analysis was implemented to show what provinces were hot spot regions and which of them
were low risk areas across Iran. Fig. 3 presents that hot spot clusters were mainly located in central parts of Iran, with 99% of
confidence levels, including Qom, Alborz, Tehran, Markazi, Isfahan, Mazandaran, Qazvin, Hamedan, Gilan, and Zanjan with
the highest rates of incidence in Iran. Moreover, Lorestan, and Kurdistan, located in western part of Iran, were other hotspots
with a confidence level of 95%. However, Kerman, and Sistan and Baluchistan were low-risk provinces due to the confidence
level of 95% as cold spots due to their lowest rates of incidence. Eastern parts of Iran showed not significant results in terms of
cold spots or hot spots, except South Khorasan, as a cold spot province with a confidence level of 90%.
5