Page 607 - NGTU_paper_withoutVideo
P. 607
Modern Geomatics Technologies and Applications
Overall accuracy is the proportion of correctly classified samples among all predicted samples. It indicates the
classifier’s quality to correctly identify samples, as shown in (4) [18]:
+ + +
= (4)
Kappa is an agreement measure between observed and predicted classes for cases in the test set, ranging from -1 to 1. It
can be calculated via (5) [18]:
× ∑ 4 − ∑ 4
= =1 =1 , (5)
2
− ∑ 4 =1
where are the diagonal elements of the confusion matrix.
Given all the predicted labels for Class , precision of the class determines the number of correctly classified samples,
using the following (6) [20]:
= (6)
Moreover, class recall is the ratio of correctly classified samples divided by the number of samples in the actual class.
The formula is given in (7) [20]:
= (7)
F-measure or F-score is the harmonic mean of Precision and Recall. It ranges from 0 to the optimal value 1, using the
following (9) [21]:
×
− = 2 × (8)
+
5. Experimental Results
In this section, the decision tree algorithms were compared to each other in the prediction process. Classification
evaluation metrics explained in section 4.2 were used for the comparisons. The computer specifications used in this study are:
Intel® Pentium® CPU B970 @ 3.30 GHz with 8 GB RAM. The fatality severity of the crashes was predicted with two decision
tree classification models. For better performance, all of the variables were normalized. Both models were trained by 10-fold
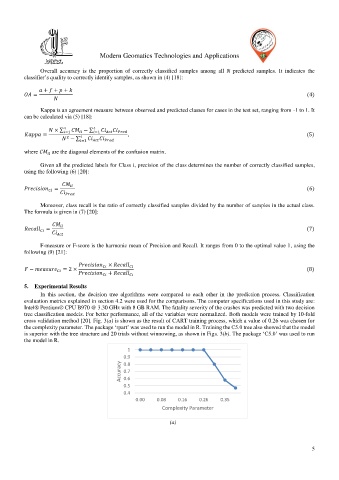
cross validation method [20]. Fig. 3(a) is shown as the result of CART training process, which a value of 0.26 was chosen for
the complexity parameter. The package ‘rpart’ was used to run the model in R. Training the C5.0 tree also showed that the model
is superior with the tree structure and 20 trials without winnowing, as shown in Figs. 3(b). The package ‘C5.0’ was used to run
the model in R.
1
0.9
Accuracy 0.7
0.8
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.00 0.08 0.16 0.26 0.35
Complexity Parameter
(a)
5