Page 7 - NGTU_paper_withoutVideo
P. 7
Modern Geomatics Technologies and Applications
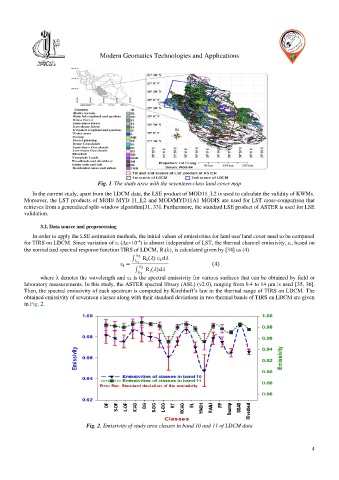
Fig. 1. The study area with the seventeen-class land cover map
In the current study, apart from the LDCM data, the LSE product of MOD11_L2 is used to calculate the validity of KWMs.
Moreover, the LST products of MOD/ MYD 11_L2 and MOD/MYD11A1 MODIS are used for LST cross-comparison that
retrieves from a generalized split-window algorithm[31, 33]. Furthermore, the standard LSE product of ASTER is used for LSE
validation.
3.2. Data source and preprocessing
In order to apply the LSE estimation methods, the initial values of emissivities for land use/ land cover need to be computed
for TIRS on LDCM. Since variation of ε i (∆ε=10 ) is almost independent of LST, the thermal channel emissivity, ε i, based on
-4
the normalized spectral response function TIRS of LDCM, R i(), is calculated given by [34] as (4).
2
∫ R ()
i
= 1 (4)
i
∫ 2 R ()
i
1
where λ denotes the wavelength and ε λ is the spectral emissivity for various surfaces that can be obtained by field or
laboratory measurements. In this study, the ASTER spectral library (ASL) (v2.0), ranging from 0.4 to 14 μm is used [35, 36].
Then, the spectral emissivity of each spectrum is computed by Kirchhoff’s law in the thermal range of TIRS on LDCM. The
obtained emissivity of seventeen classes along with their standard deviations in two thermal bands of TIRS on LDCM are given
in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. Emissivity of study area classes in band 10 and 11 of LDCM data
4