Page 15 - Poster presentation KVAC 22
P. 15
The 22nd Khon Kaen Veterinary Annual International Conference 2021
Academic Achievements of
INTER-PROFESSIONAL LEARING on
Antimicrobial Resistance & Stewardship
for Thai Future Workforces from
Veterinary and Health Sciences, Chiang Mai University Raktham Mektrirat 1,2, *
Tongkorn Meeyam 1
1 Department of Veterinary Biosciences and Veterinary Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Penkarn Kanjanarat 2
2 Epidemiology Research Group of Infectious Disease, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Wasan Katip 2, 3
3 Department of Pharmaceutical Care, Faculty of Pharmacy, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
Introduction Objective
An expanding amount of data is being documented on antimicrobial resistance (AMR) worldwide, with consequent economic The present study aims to develop the IPE
impact and public health concerns [1]. AMR is a comprehensive problem related to the humans, the animals, and the environment. curriculum using team-based approach to
The environmental contamination of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria creates a consensual concern in the scientific community and address challenges of AMR for training of
the One Health (OH) approach [2]. The interdisciplinary skills and competences are necessary for in-service current workforces who undergraduate veterinary and health science
work in a collaborative health team environment for AMR prevention and control [3]. To efficiently combat AMR problem, the pre- students, Chiang Mai University (CMU),
service students of health sciences need to be prepared through the interprofessional education (IPE). Thailand.
Methodology Data were categorized and analyzed
A working group of academic The concepts and structure of by using descriptive statistics.
instructors conducted a short- one-day course includes the The Wilcoxon matched pairs signed
course training to initiate a impacts of antimicrobial use in rank test was used to assess the
curriculum & the activities on human and animals, the differences between the pre- and
multidisciplinary managements community acquired AMR, the post-lesson test on the knowledge.
for human and animal health managements of AMR using OH The Mann-Whitney U test was used
by combining the One Health approach, and the system to compare on the awareness and
Core Competency (OHCC). mapping for AMR solutions.. the IPE competency results.
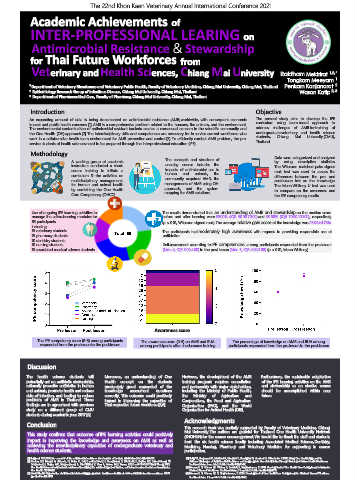
Use of ongoing IPE learning activities to The results demonstrated that an understanding of AMR and stewardship on the median score
manage the active-learning modules for before and after learning were 60.00% (IQR 50.00-70.00) and 90.00% (IQR 70.00-100.00), respectively
65 participants (p < 0.01, Wilcoxon signed rank). The average relative gain score of the knowledge was 23.04±4.78%.
including
15 veterinary students. The participants had moderately high awareness with regards to providing responsible use of
15 pharmacy students. antibiotics.
10 dentistry students.
10 nursing students. Self-assessment according to IPE competencies among participants responded from the pre-lesson
15 associated medical science students. (Mdn 4, IQR 3.00-4.00) to the post-lesson (Mdn 5, IQR 4.00-5.00) (p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney).
Awareness score
The IPE competency score (0-5) among participants The awareness score (0-5) on AMR and RUA The percentage of knowledge on AMR and RUA among
responded from the pre-lesson to the post-lesson among participants after short-course training participants responded from the pre-lesson to the post-lesson
Discussion
The health science students will Moreover, an understanding of One However, the development of the AMR Furthermore, the sustainable adaptation
potentially act on antibiotic stewardship, Health concept on the students training program requires consultation of the IPE learning activities on the AMR
rationally prescribe antibiotics in human moderately good responded of the and partnership with major stakeholders, and stewardship as an elective course
and animals, promote health and reduce knowledge assessment questions including the Ministry of Public Health, should be accomplished within near
risks of infection, and leading to reduce correctly. This outcome could positively the Ministry of Agriculture and future
problems of AMR in Thailand. These impact in improving the capacities of Cooperatives, the Food and Agriculture
findings are in agreement with previous Thai respective future workforce [5,6]. Organization (FAO), and the World
study on a different group of CMU Organization for Animal Health (OIE).
students during academic year 2017 [4].
Acknowledgments
Conclusion This research work was partially supported by Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Chiang
This study confirms that outcome of IPE learning activities could positively Mai University. The authors are grateful for Thailand One Health University Network
(THOHUN) for the course encouragement. We would like to thank the staff and students
impact in improving the knowledge and awareness on AMR as well as from the six health science faculty including Associated Medical Science, Dentistry,
achieving the interdisciplinary capacities of undergraduate veterinary and Medicine, Nursing, Pharmacy and Veterinary Medicine for supporting in course
health science students. participation.
[1] Reygaert, W.C. 2018. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 4(3): 482-501. [4] Katip W., Kanjanarat P., Mektrirat R., Meeyam T., Kasatpibal N., Anukool U., Oberdorfer P. 2018. Using One Health Approach to
[2] Booton, R.D., Meeyai, A., Alhusein, N., Buller, H., Feil, E. and Lambert, H., Mongkolsuk, S., Pitchforth, E., Reyher, K.K., Sakcamduang, W., Address Challenges of Antimicrobial Resistance and Inappropriate Use of Antibiotics Through Training of Future Health Workforces.
.
.
.
Satayavivad, J., Singer, A.C., Sringernyuang, L., Thamlikitkul, V., Vass, L., Avison, M.B., Turner, K.M.E. and OH-DART Study Group. 2021. Southeast Asian J rop Med Public Health. 49(1):36-42.
One health drivers of antibacterial resistance: Quantifying the relative impacts of human, animal and environmental use transmission. [5] Moonsom, S., Chavez, I.F., Waters, K., Fenwick, S., Singhasivanon, P. 2018. Development of One Health Core Competency domains for
One Health, 12: 100220 Thailand Current Workforce. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 49(1):12-15.
.
.
.
[3] World Health Organization. Antimicrobial stewardship programs in health-care facilities in low- and middle-income countries: a WHO [6] Moonsom, S., Chavez, I.F., S., Singhasivanon, P. 2018. Development of One Health Core Competency for Thailand Current Workforce.
.
.
.
practical toolkit. 2019. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 49(1): 16-19.