Page 8 - Natural Pesticides PDF Flipbook
P. 8
Oguh et al.; AJBGE, 2(3): 1-18, 2019; Article no.AJBGE.53356
1
with acetylcholine, the major neurotransmitter, 3 mg kg−1), but commercial preparations
by bonding to acetylcholine receptors at nerve typically contain less than 1% active ingredient,
synapses and causing uncontrolled nerve roviding a margin of safety. These alkaloids are
p
firing. This disruption of normal nerve impulse remarkably similar to that of the pyrethrins,
activity results in rapid failure of those eir lack of structural similarity. Sabadilla
it
e
th
p
d
e
s
body systems that depend on nervous input for is used primarily by organic growers; in California
proper functioning. In insects, the action of about 100 kg is used annually, primarily on citrus
o
r
nicotine is fairly selective, and only certain ps and avocado [19].
c
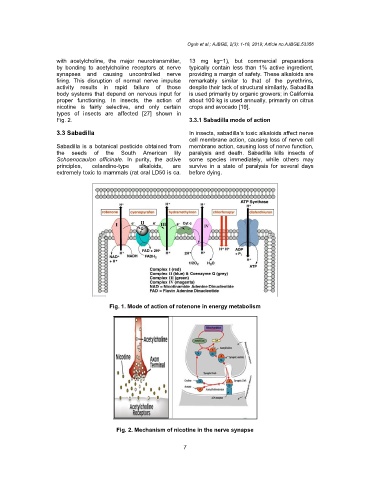
types of insects are affected [27] shown in
Fig. 2. 3.3.1 Sabadilla mode of action
3.3 Sabadilla In insects, sabadilla’s toxic alkaloids affect nerve
cell membrane action, causing loss of nerve cell
Sabadilla is a botanical pesticide obtained from membrane action, causing loss of nerve function,
the seeds of the South American lily paralysis and death. Sabadilla kills insects of
Schoenocaulon officinale. In purity, the active some species immediately, while others may
principles, celandine-type alkaloids, are survive in a state of paralysis for several days
extremely toxic to mammals (rat oral LD50 is ca. before dying.
Fig. 1. Mode of action of rotenone in energy metabolism
Fig. 2. Mechanism of nicotine in the nerve synapse
7