Page 87 - e-book CPG - Bipolar Disorder
P. 87
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES MANAGEMENT OF BIPOLAR DISORDER (2ND ED.)
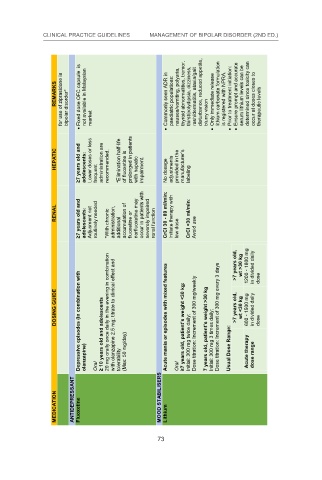
for use of ziprasidone in bipolar disorder* Fixed dose OFC capsule is not available in Malaysian market Commonly seen ADR in paediatric populations: blurry vision Only immediate release is registered with NPRA. Prior to treatment initiation: occur at doses closes to therapeutic levels
REMARKS nausea/vomiting, polyuria, thyroid abnormalities, tremor, thirst/polydipsia, dizziness, rash/dermatitis, ataxia/gait disturbance, reduced appetite, lithium carbonate formulation Ensure prompt and accurate serum lithium levels can be determined since toxicity can
HEPATIC ≥7 years old and adolescents: Lower doses or less frequent administration are recommended. *Elimination half-life of fluoxetine is prolonged in patients with hepatic impairment. No dosage adjustments provided in the manufacturer’s labeling
≥7 years old and adolescents: Adjusment not routinely needed *With chronic administration, additional accumulation of fluoxetine or norfluoxetine may severely impaired renal function Initiate therapy with low dose CrCl <30 ml/min: Avoid use 73
RENAL occur in patients with CrCl 30 - 89 ml/min:
Depressive episodes (in combination with olanzapine) ≥ 10 years old and adolescents with olanzapine 2.5 mg; titrate to clinical effect and tolerability (Max: 50 mg/day) Acute mania or episodes with mixed features ≥7 years old, patient’s weight <30 kg: Initial: 300 mg twice daily; Dose titratio
DOSING GUIDE 20 mg orally once daily in the evening in combination >7 years old, >7 years old, wt >30 kg wt <30 kg 1200 - 1800 mg 600 - 1500 mg in divided daily in divided daily dose
MEDICATION ANTIDEPRESSANT Fluoxetine Oral MOOD STABILISERS Lithium Oral
73