Page 146 - Interactive Theoritical Notes of Bioharmaceutics and pharamcokinetics.docx compressed
P. 146
PharmD clinical pharmacy program Level 3, Semester 2 Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics (PT608(
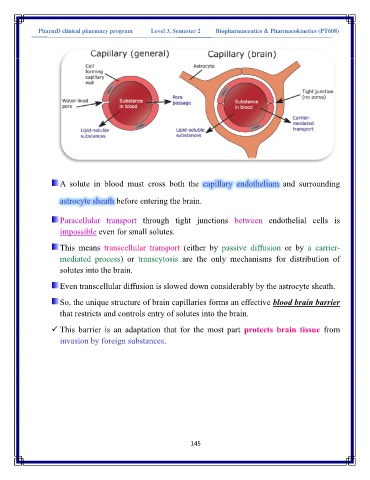
A solute in blood must cross both the capillary endothelium and surrounding
astrocyte sheath before entering the brain.
Paracellular transport through tight junctions between endothelial cells is
impossible even for small solutes.
This means transcellular transport (either by passive diffusion or by a carrier-
mediated process) or transcytosis are the only mechanisms for distribution of
solutes into the brain.
Even transcellular diffusion is slowed down considerably by the astrocyte sheath.
So, the unique structure of brain capillaries forms an effective blood brain barrier
that restricts and controls entry of solutes into the brain.
✓ This barrier is an adaptation that for the most part protects brain tissue from
invasion by foreign substances.
145