Page 45 - C:\Users\Abdul Kadir Bagis\Documents\Flip PDF Corporate Edition\Abdul Kadir Bagis, M. Pds\
P. 45
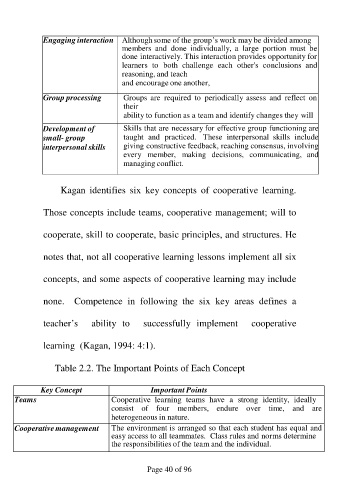
Engaging interaction Although some of the group’s work may be divided among
members and done individually, a large portion must be
done interactively. This interaction provides opportunity for
learners to both challenge each other's conclusions and
reasoning, and teach
and encourage one another,
Group processing Groups are required to periodically assess and reflect on
their
ability to function as a team and identify changes they will
Development of Skills that are necessary for effective group functioning are
small- group taught and practiced. These interpersonal skills include
interpersonal skills giving constructive feedback, reaching consensus, involving
every member, making decisions, communicating, and
managing conflict.
Kagan identifies six key concepts of cooperative learning.
Those concepts include teams, cooperative management; will to
cooperate, skill to cooperate, basic principles, and structures. He
notes that, not all cooperative learning lessons implement all six
concepts, and some aspects of cooperative learning may include
none. Competence in following the six key areas defines a
teacher’s ability to successfully implement cooperative
learning (Kagan, 1994: 4:1).
Table 2.2. The Important Points of Each Concept
Key Concept Important Points
Teams Cooperative learning teams have a strong identity, ideally
consist of four members, endure over time, and are
heterogeneous in nature.
Cooperative management The environment is arranged so that each student has equal and
easy access to all teammates. Class rules and norms determine
the responsibilities of the team and the individual.
Page 40 of 96