Page 47 - C:\Users\Abdul Kadir Bagis\Documents\Flip PDF Corporate Edition\Abdul Kadir Bagis, M. Pds\
P. 47
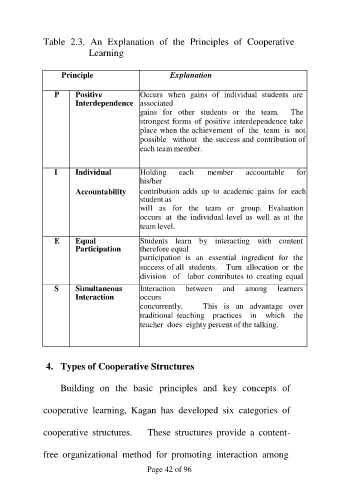
Table 2.3. An Explanation of the Principles of Cooperative
Learning
Principle Explanation
P Positive Occurs when gains of individual students are
Interdependence associated
gains for other students or the team. The
strongest forms of positive interdependence take
place when the achievement of the team is not
possible without the success and contribution of
each team member.
I Individual Holding each member accountable for
his/her
Accountability contribution adds up to academic gains for each
student as
will as for the team or group. Evaluation
occurs at the individual level as well as at the
team level.
E Equal Students learn by interacting with content
Participation therefore equal
participation is an essential ingredient for the
success of all students. Turn allocation or the
division of labor contributes to creating equal
S Simultaneous Interaction between and among learners
Interaction occurs
concurrently. This is an advantage over
traditional teaching practices in which the
teacher does eighty percent of the talking.
4. Types of Cooperative Structures
Building on the basic principles and key concepts of
cooperative learning, Kagan has developed six categories of
cooperative structures. These structures provide a content-
free organizational method for promoting interaction among
Page 42 of 96