Page 23 - Mesenchymal Stem cells, Exosomes and vitamins in the fight aginst COVID
P. 23
Al-Khawaga and Abdelalim Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2020) 11:437 Page 4 of 33
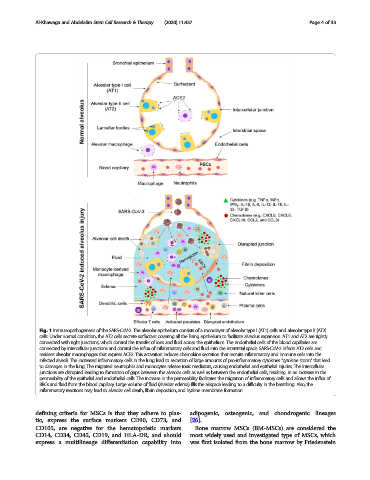
Fig. 1 Immunopathogenesis of the SARS-CoV-2. The alveolar epithelium consists of a monolayer of alveolar type I (AT1) cells and alveolar type II (AT2)
cells. Under normal condition, the AT2 cells secrete surfactant covering all the lining epithelium to facilitate alveolus expansion. AT1 and AT2 are tightly
connected with tight junctions, which control the transfer of ions and fluid across the epithelium. The endothelial cells of the blood capillaries are
connected by intercellular junctions and control the influx of inflammatory cells and fluid into the interstitial space. SARS-CoV-2 infects AT2 cells and
resident alveolar macrophages that express ACE2. This activation induces chemokine secretion that recruits inflammatory and immune cells into the
infected alveoli. The increased inflammatory cells in the lung lead to secretion of large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines “cytokine storm” that lead
to damages in the lung. The migrated neutrophils and monocytes release toxic mediators, causing endothelial and epithelial injuries. The intercellular
junctions are disrupted leading to formation of gaps between the alveolar cells as well as between the endothelial cells, resultinginanincreaseinthe
permeability of the epithelial and endothelial cells. The increase in the permeability facilitates the migration of inflammatory cells and allows the influx of
RBCs and fluid from the blood capillary. Large volume of fluid (alveolar edema) fills the airspace leading to a difficulty in the breathing. Also, the
inflammatory reactions may lead to alveolar cell death, fibrin deposition, and hyaline membrane formation
defining criteria for MSCs is that they adhere to plas- adipogenic, osteogenic, and chondrogenic lineages
tic, express the surface markers CD90, CD73, and [26].
CD105, are negative for the hematopoietic markers Bone marrow MSCs (BM-MSCs) are considered the
CD14, CD34, CD45, CD19, and HLA-DR, and should most widely used and investigated type of MSCs, which
express a multilineage differentiation capability into was first isolated from the bone marrow by Friedenstein