Page 24 - Mesenchymal Stem cells, Exosomes and vitamins in the fight aginst COVID
P. 24
Al-Khawaga and Abdelalim Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2020) 11:437 Page 5 of 33
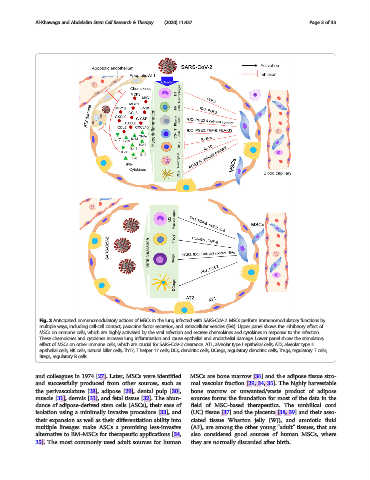
Fig. 2 Anticipated immunomodulatory actions of MSCs in the lung infected with SARS-CoV-2. MSCs perform immunomodulatory functions by
multiple ways, including cell-cell contact, paracrine factor secretion, and extracellular vesicles (EVs). Upper panel shows the inhibitory effectof
MSCs on immune cells, which are highly activated by the viral infection and secrete chemokines and cytokines in response to the infection.
These chemokines and cytokines increase lung inflammation and cause epithelial and endothelial damage. Lower panel show the stimulatory
effect of MSCs on other immune cells, which are crucial for SARS-CoV-2 clearance. AT1, alveolar type I epithelial cells; AT2, alveolar type II
epithelial cells; NK cells, natural killer cells; Th17, T helper 17 cells; DCs, dendritic cells; DCregs, regulatory dendritic cells; Tregs, regulatory T cells;
Bregs, regulatory B cells
and colleagues in 1974 [27]. Later, MSCs were identified MSCs are bone marrow [36] and the adipose tissue stro-
and successfully produced from other sources, such as mal vascular fraction [29, 34, 35]. The highly harvestable
the perivasculature [28], adipose [29], dental pulp [30], bone marrow or unwanted/waste product of adipose
muscle [31], dermis [31], and fetal tissue [32]. The abun- sources forms the foundation for most of the data in the
dance of adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs), their ease of field of MSC-based therapeutics. The umbilical cord
isolation using a minimally invasive procedure [33], and (UC) tissue [37] and the placenta [38, 39] and their asso-
their expansion as well as their differentiation ability into ciated tissue Wharton jelly (WJ), and amniotic fluid
multiple lineages make ASCs a promising less-invasive (AF), are among the other young “adult” tissues, that are
alternative to BM-MSCs for therapeutic applications [34, also considered good sources of human MSCs, where
35]. The most commonly used adult sources for human they are normally discarded after birth.