Page 32 - Towards A Sustainable Future , Phase 3 2025, E-Book_Neat
P. 32
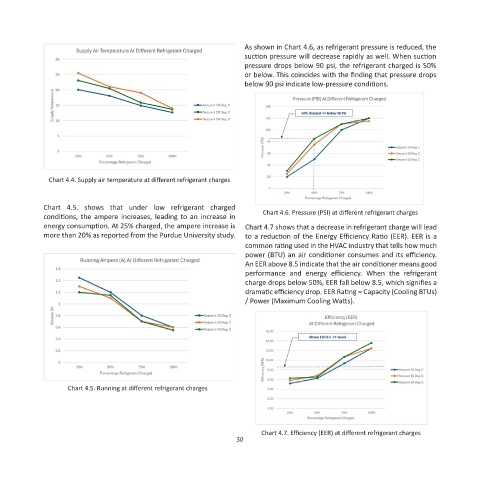
As shown in Chart 4.6, as refrigerant pressure is reduced, the
suction pressure will decrease rapidly as well. When suction
pressure drops below 90 psi, the refrigerant charged is 50%
or below. This coincides with the finding that pressure drops
below 90 psi indicate low-pressure conditions.
Chart 4.4. Supply air temperature at different refrigerant charges
Chart 4.5. shows that under low refrigerant charged Chart 4.6. Pressure (PSI) at different refrigerant charges
conditions, the ampere increases, leading to an increase in
energy consumption. At 25% charged, the ampere increase is Chart 4.7 shows that a decrease in refrigerant charge will lead
more than 20% as reported from the Purdue University study. to a reduction of the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER). EER is a
common rating used in the HVAC industry that tells how much
power (BTU) an air conditioner consumes and its efficiency.
An EER above 8.5 indicate that the air conditioner means good
performance and energy efficiency. When the refrigerant
charge drops below 50%, EER fall below 8.5, which signifies a
dramatic efficiency drop. EER Rating = Capacity (Cooling BTUs)
/ Power (Maximum Cooling Watts).
Chart 4.5. Running at different refrigerant charges
Chart 4.7. Efficiency (EER) at different refrigerant charges
30