Page 174 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 174
164 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
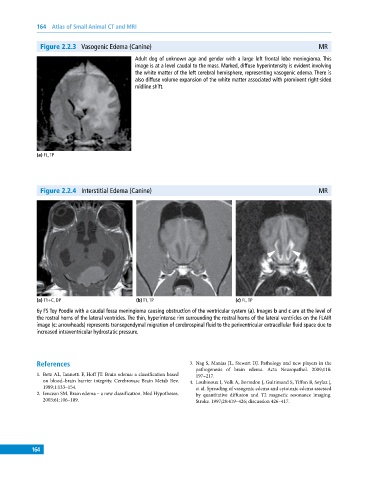
Figure 2.2.3 Vasogenic Edema (Canine) MR
Adult dog of unknown age and gender with a large left frontal lobe meningioma. This
image is at a level caudal to the mass. Marked, diffuse hyperintensity is evident involving
the white matter of the left cerebral hemisphere, representing vasogenic edema. There is
also diffuse volume expansion of the white matter associated with prominent right‐sided
midline shift.
(a) FL, TP
Figure 2.2.4 Interstitial Edema (Canine) MR
(a) T1+C, DP (b) T1, TP (c) FL, TP
6y FS Toy Poodle with a caudal fossa meningioma causing obstruction of the ventricular system (a). Images b and c are at the level of
the rostral horns of the lateral ventricles. The thin, hyperintense rim surrounding the rostral horns of the lateral ventricles on the FLAIR
image (c: arrowheads) represents transependymal migration of cerebrospinal fluid to the periventricular extracellular fluid space due to
increased intraventricular hydrostatic pressure.
References 3. Nag S, Manias JL, Stewart DJ. Pathology and new players in the
pathogenesis of brain edema. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118:
1. Betz AL, Iannotti F, Hoff JT. Brain edema: a classification based 197–217.
on blood–brain barrier integrity. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 4. Loubinoux I, Volk A, Borredon J, Guirimand S, Tiffon B, Seylaz J,
1989;1:133–154. et al. Spreading of vasogenic edema and cytotoxic edema assessed
2. Iencean SM. Brain edema – a new classification. Med Hypotheses. by quantitative diffusion and T2 magnetic resonance imaging.
2003;61:106–109. Stroke. 1997;28:419–426; discussion 426–417.
164