Page 13 - E-book Digestive System
P. 13
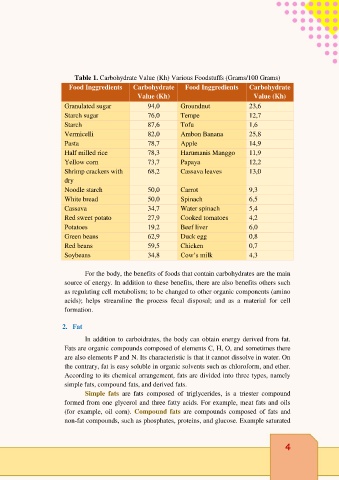
Table 1. Carbohydrate Value (Kh) Various Foodstuffs (Grams/100 Grams)
Food Inggredients Carbohydrate Food Inggredients Carbohydrate
Value (Kh) Value (Kh)
Granulated sugar 94,0 Groundnut 23,6
Starch sugar 76,0 Tempe 12,7
Starch 87,6 Tofu 1,6
Vermicelli 82,0 Ambon Banana 25,8
Pasta 78,7 Apple 14,9
Half milled rice 78,3 Harumanis Manggo 11,9
Yellow corn 73,7 Papaya 12,2
Shrimp crackers with 68,2 Cassava leaves 13,0
dry
Noodle starch 50,0 Carrot 9,3
White bread 50,0 Spinach 6,5
Cassava 34,7 Water spinach 5,4
Red sweet potato 27,9 Cooked tomatoes 4,2
Potatoes 19,2 Beef liver 6,0
Green beans 62,9 Duck egg 0,8
Red beans 59,5 Chicken 0,7
Soybeans 34,8 Cow’s milk 4,3
For the body, the benefits of foods that contain carbohydrates are the main
source of energy. In addition to these benefits, there are also benefits others such
as regulating cell metabolism; to be changed to other organic components (amino
acids); helps streamline the process fecal disposal; and as a material for cell
formation.
2. Fat
In addition to carboidrates, the body can obtain energy derived from fat.
Fats are organic compounds composed of elements C, H, O, and sometimes there
are also elements P and N. Its characteristic is that it cannot dissolve in water. On
the contrary, fat is easy soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, and ether.
According to its chemical arrangement, fats are divided into three types, namely
simple fats, compound fats, and derived fats.
Simple fats are fats composed of triglycerides, is a triester compound
formed from one glycerol and three fatty acids. For example, meat fats and oils
(for example, oil corn). Compound fats are compounds composed of fats and
non-fat compounds, such as phosphates, proteins, and glucose. Example saturated
4