Page 362 - Kitab3DsMax
P. 362
Part III: Modeling Basics
Other parameters include the Radius and the From and To settings, where you can enter the value in
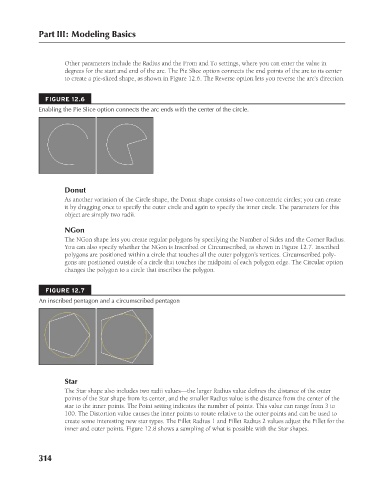
degrees for the start and end of the arc. The Pie Slice option connects the end points of the arc to its center
to create a pie-sliced shape, as shown in Figure 12.6. The Reverse option lets you reverse the arc’s direction.
FIGURE 12.6
Enabling the Pie Slice option connects the arc ends with the center of the circle.
Donut
As another variation of the Circle shape, the Donut shape consists of two concentric circles; you can create
it by dragging once to specify the outer circle and again to specify the inner circle. The parameters for this
object are simply two radii.
NGon
The NGon shape lets you create regular polygons by specifying the Number of Sides and the Corner Radius.
You can also specify whether the NGon is Inscribed or Circumscribed, as shown in Figure 12.7. Inscribed
polygons are positioned within a circle that touches all the outer polygon’s vertices. Circumscribed poly-
gons are positioned outside of a circle that touches the midpoint of each polygon edge. The Circular option
changes the polygon to a circle that inscribes the polygon.
FIGURE 12.7
An inscribed pentagon and a circumscribed pentagon
Star
The Star shape also includes two radii values—the larger Radius value defines the distance of the outer
points of the Star shape from its center, and the smaller Radius value is the distance from the center of the
star to the inner points. The Point setting indicates the number of points. This value can range from 3 to
100. The Distortion value causes the inner points to rotate relative to the outer points and can be used to
create some interesting new star types. The Fillet Radius 1 and Fillet Radius 2 values adjust the Fillet for the
inner and outer points. Figure 12.8 shows a sampling of what is possible with the Star shapes.
314
6/30/10 4:20 PM
19_617779-ch12.indd 314 6/30/10 4:20 PM
19_617779-ch12.indd 314