Page 17 - E-LKM ACID BASE
P. 17
Lembar Kerja Mahasiswa - Asam Basa
In this case, the water is behaving as a base, because its lone pair
seeks out a positive charge (the proton), while the hydrochloric acid,
HCl, behaves as an acid, because it accepts the lone pair.
(Suchocki, 2014)
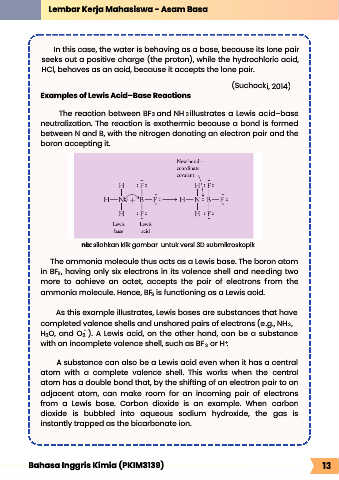
Examples of Lewis Acid–Base Reactions
The reaction between BF and NH illustrates a Lewis acid–base
3
3
neutralization. The reaction is exothermic because a bond is formed
between N and B, with the nitrogen donating an electron pair and the
boron accepting it.
nb: silahkan klik gambar untuk versi 3D submikroskopik
The ammonia molecule thus acts as a Lewis base. The boron atom
in BF , having only six electrons in its valence shell and needing two
3
more to achieve an octet, accepts the pair of electrons from the
ammonia molecule. Hence, BF is functioning as a Lewis acid.
3
As this example illustrates, Lewis bases are substances that have
completed valence shells and unshared pairs of electrons (e.g., NH ,
3
-
H O, and O ). A Lewis acid, on the other hand, can be a substance
2
2
with an incomplete valence shell, such as BF or H .
+
3
A substance can also be a Lewis acid even when it has a central
atom with a complete valence shell. This works when the central
atom has a double bond that, by the shifting of an electron pair to an
adjacent atom, can make room for an incoming pair of electrons
from a Lewis base. Carbon dioxide is an example. When carbon
dioxide is bubbled into aqueous sodium hydroxide, the gas is
instantly trapped as the bicarbonate ion.
Bahasa Inggris Kimia (PKIM3139) 13