Page 20 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 20
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
2.2 The Audit Process
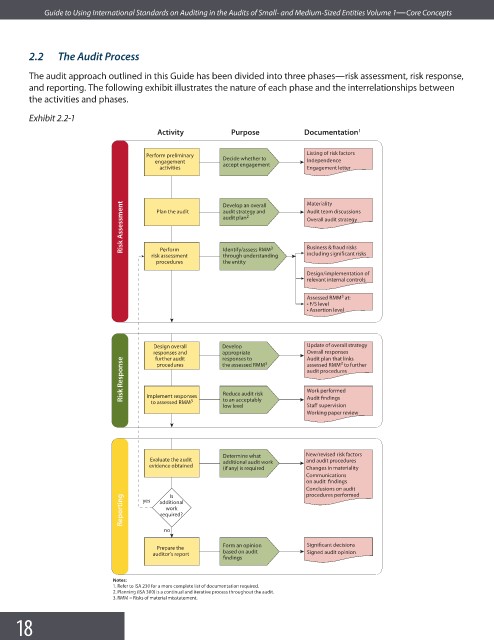
The audit approach outlined in this Guide has been divided into three phases—risk assessment, risk response,
and reporting. The following exhibit illustrates the nature of each phase and the interrelationships between
the activities and phases.
Exhibit 2.2-1
Activity Purpose Documentation 1
Listing of risk factors
Perform preliminary Decide whether to
engagement accept engagement Independence
activities Engagement letter
Risk Assessment Plan the audit Develop an overall Materiality
Audit team discussions
audit strategy and
2
audit plan
Overall audit strategy
Perform
including significant risks
risk assessment Identify/assess RMM 3 Business & fraud risks
through understanding
procedures the entity
Design/implementation of
relevant internal controls
3
Assessed RMM at:
t F/S level
t Assertion level
Design overall Develop Update of overall strategy
responses and appropriate 3 Overall responses
Audit plan that links
responses to
further audit
Risk Response audit procedures
3
the assessed RMM
assessed RMM to further
procedures
Work performed
Implement responses
to an acceptably
to assessed RMM 3 Reduce audit risk Audit findings
low level Staff supervision
Working paper review
Determine what New/revised risk factors
Evaluate the audit additional audit work and audit procedures
evidence obtained
(if any) is required Changes in materiality
Communications
on audit findings
Conclusions on audit
procedures performed
Is
Reporting yes additional
work
required?
no
Form an opinion Significant decisions
Prepare the
auditor’s report based on audit Signed audit opinion
findings
Notes:
1. Refer to ISA 230 for a more complete list of documentation required.
2. Planning (ISA 300) is a continual and iterative process throughout the audit.
3. RMM = Risks of material misstatement.
18