Page 25 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 25
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
Scope of an Audit
The scope of the auditor’s work and the opinion provided are usually confined to whether the fi nancial
statements are prepared, in all material respects, in accordance with the applicable fi nancial reporting
framework. As a result, an unmodified auditor’s report does not provide any assurance about the future viability
of the entity, nor the effi ciency or effectiveness with which management has conducted the affairs of the entity.
Any extension of this basic audit responsibility, such as that required by local laws or securities regulations,
would require the auditor to undertake further work and to modify or expand the auditor’s report
accordingly.
Material Misstatements
A material misstatement (the aggregate of all uncorrected misstatements and missing/misleading disclosures
in the financial statements, including omissions) has occurred when they could reasonably be expected to
influence the economic decisions of users made on the basis of the fi nancial statements.
Assertions
Assertions are representations by management, explicit or otherwise, that are embodied in the fi nancial
statements. They relate to the recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of the various
elements (amounts and disclosures) in the financial statements. For example, the completeness assertion
relates to all transactions and events that should have been recorded having been recorded. They are used
by the auditor to consider the different types of potential misstatements that may occur.
3.2 Audit Risk
Audit risk is the risk of expressing an inappropriate audit opinion on financial statements that are materially
misstated. The objective of the audit is to reduce this audit risk to an acceptably low level.
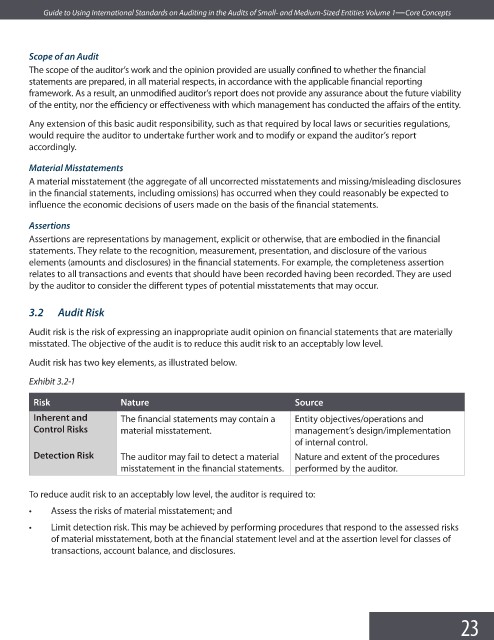
Audit risk has two key elements, as illustrated below.
Exhibit 3.2-1
Risk Nature Source
Inherent and The financial statements may contain a Entity objectives/operations and
Control Risks material misstatement. management’s design/implementation
of internal control.
Detection Risk The auditor may fail to detect a material Nature and extent of the procedures
misstatement in the fi nancial statements. performed by the auditor.
To reduce audit risk to an acceptably low level, the auditor is required to:
• Assess the risks of material misstatement; and
• Limit detection risk. This may be achieved by performing procedures that respond to the assessed risks
of material misstatement, both at the financial statement level and at the assertion level for classes of
transactions, account balance, and disclosures.
23