Page 26 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 26
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
Audit Risk Components
The major components of audit risk are described in the exhibit below.
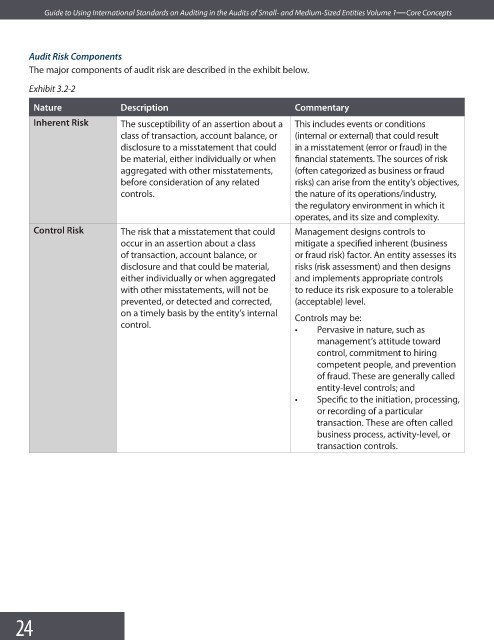
Exhibit 3.2-2
Nature Description Commentary
Inherent Risk The susceptibility of an assertion about a This includes events or conditions
class of transaction, account balance, or (internal or external) that could result
disclosure to a misstatement that could in a misstatement (error or fraud) in the
be material, either individually or when financial statements. The sources of risk
aggregated with other misstatements, (often categorized as business or fraud
before consideration of any related risks) can arise from the entity’s objectives,
controls. the nature of its operations/industry,
the regulatory environment in which it
operates, and its size and complexity.
Control Risk The risk that a misstatement that could Management designs controls to
occur in an assertion about a class mitigate a specified inherent (business
of transaction, account balance, or or fraud risk) factor. An entity assesses its
disclosure and that could be material, risks (risk assessment) and then designs
either individually or when aggregated and implements appropriate controls
with other misstatements, will not be to reduce its risk exposure to a tolerable
prevented, or detected and corrected, (acceptable) level.
on a timely basis by the entity’s internal
Controls may be:
control.
• Pervasive in nature, such as
management’s attitude toward
control, commitment to hiring
competent people, and prevention
of fraud. These are generally called
entity-level controls; and
• Specific to the initiation, processing,
or recording of a particular
transaction. These are often called
business process, activity-level, or
transaction controls.
24