Page 29 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 29
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
3.3 How to Perform a Risk-Based Audit
Paragraph # Relevant Extracts from ISAs
200.15 The auditor shall plan and perform an audit with professional skepticism recognizing that
circumstances may exist that cause the financial statements to be materially misstated. (Ref:
Para. A18-A22)
200.16 The auditor shall exercise professional judgment in planning and performing an audit of
financial statements. (Ref: Para. A23-A27)
200.17 To obtain reasonable assurance, the auditor shall obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence
to reduce audit risk to an acceptably low level and thereby enable the auditor to draw
reasonable conclusions on which to base the auditor’s opinion. (Ref: Para. A28-A52)
200.21 To achieve the overall objectives of the auditor, the auditor shall use the objectives stated in
relevant ISAs in planning and performing the audit, having regard to the interrelationships
among the ISAs, to: (Ref: Para. A67-A69)
(a) Determine whether any audit procedures in addition to those required by the ISAs are
necessary in pursuance of the objectives stated in the ISAs; and (Ref: Para. A70)
(b) Evaluate whether sufficient appropriate audit evidence has been obtained. (Ref: Para. A71)
A risk-based audit has three key steps, as illustrated below.
Exhibit 3.3-1
Steps (Phases) Description
Risk Assessment Performing risk assessment procedures to identify and assess the risks of material
misstatement in the fi nancial statements.
Risk Response Designing and performing further audit procedures that respond to identifi ed and
assessed risks of material misstatement, at both the financial statement and assertion
levels.
Reporting This involves:
• Forming an opinion based on the audit evidence obtained; and
• Preparing and issuing a report that is appropriate to the conclusions reached.
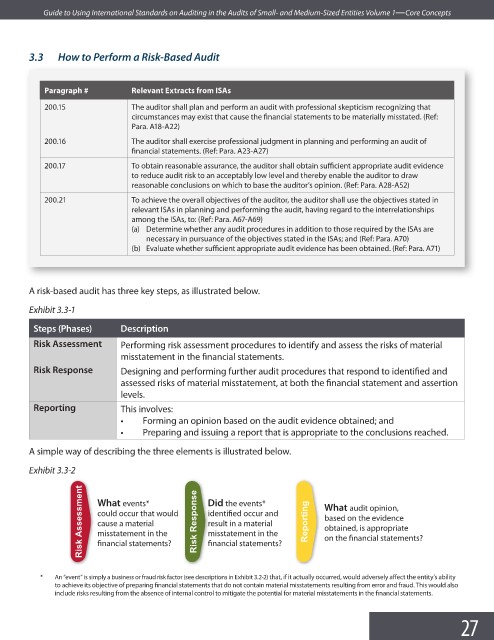
A simple way of describing the three elements is illustrated below.
Exhibit 3.3-2
Risk Assessment What events* Risk Response Did the events* Reporting What audit opinion,
identified occur and
could occur that would
based on the evidence
cause a material
result in a material
obtained, is appropriate
misstatement in the
misstatement in the
on the financial statements?
financial statements?
financial statements?
* An “event” is simply a business or fraud risk factor (see descriptions in Exhibit 3.2-2) that, if it actually occurred, would adversely affect the entity’s ability
to achieve its objective of preparing financial statements that do not contain material misstatements resulting from error and fraud. This would also
include risks resulting from the absence of internal control to mitigate the potential for material misstatements in the fi nancial statements.
27