Page 32 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 32
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
Requirements Description
Use of Professional The ISA audit requirements require the use and then documentation of signifi cant
Judgment judgments made by the auditor throughout the audit. Typical examples of tasks
throughout the risk assessment process include:
• Deciding to accept or continue with the client;
• Developing the overall audit strategy;
• Establishing materiality;
• Assessing risks of material misstatement, including the identification of signifi cant
risks and other areas where special audit consideration may be necessary; and
• Developing expectations for use when performing analytical procedures.
Risk Response
Paragraph # ISA Objective(s)
330.3 The objective of the auditor is to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding the
assessed risks of material misstatement, through designing and implementing appropriate
responses to those risks.
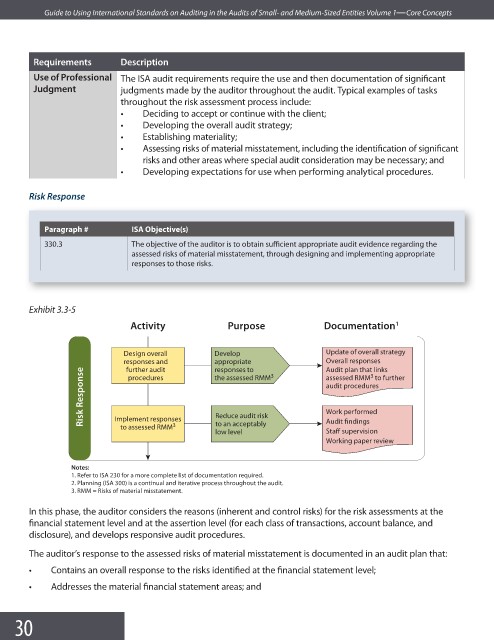
Exhibit 3.3-5
Activity Purpose Documentation 1
Design overall Develop Update of overall strategy
responses and appropriate 3 Overall responses
further audit
responses to
Audit plan that links
Risk Response audit procedures
3
assessed RMM to further
procedures
the assessed RMM
Work performed
Reduce audit risk
Implement responses
to an acceptably
3
to assessed RMM
Staff supervision
low level Audit findings
Working paper review
Notes:
1. Refer to ISA 230 for a more complete list of documentation required.
2. Planning (ISA 300) is a continual and iterative process throughout the audit.
3. RMM = Risks of material misstatement.
In this phase, the auditor considers the reasons (inherent and control risks) for the risk assessments at the
financial statement level and at the assertion level (for each class of transactions, account balance, and
disclosure), and develops responsive audit procedures.
The auditor’s response to the assessed risks of material misstatement is documented in an audit plan that:
• Contains an overall response to the risks identified at the financial statement level;
• Addresses the material financial statement areas; and
30