Page 266 - Big Data Analytics for Connected Vehicles and Smart Cities
P. 266
246 Big Data Analytics for Connected Vehicles and Smart Cities Benefit and Cost Estimation For Smart City Transportation Services 247
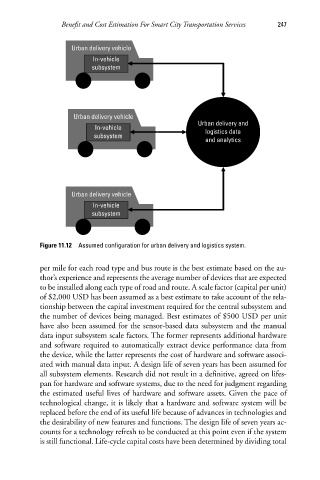
Figure 11.12 Assumed configuration for urban delivery and logistics system.
per mile for each road type and bus route is the best estimate based on the au-
thor’s experience and represents the average number of devices that are expected
to be installed along each type of road and route. A scale factor (capital per unit)
of $2,000 USD has been assumed as a best estimate to take account of the rela-
tionship between the capital investment required for the central subsystem and
the number of devices being managed. Best estimates of $500 USD per unit
have also been assumed for the sensor-based data subsystem and the manual
data input subsystem scale factors. The former represents additional hardware
and software required to automatically extract device performance data from
the device, while the latter represents the cost of hardware and software associ-
ated with manual data input. A design life of seven years has been assumed for
all subsystem elements. Research did not result in a definitive, agreed on lifes-
pan for hardware and software systems, due to the need for judgment regarding
the estimated useful lives of hardware and software assets. Given the pace of
technological change, it is likely that a hardware and software system will be
replaced before the end of its useful life because of advances in technologies and
the desirability of new features and functions. The design life of seven years ac-
counts for a technology refresh to be conducted at this point even if the system
is still functional. Life-cycle capital costs have been determined by dividing total