Page 48 - FREN-C2021 PROCEEDINGS
P. 48
To more elaborate about organizational change, According Pollack (2015), Kotter's Model have
developed eight steps that can be adopted to implement change as below:
Figure 2: Kotter’s 8 step change management Model
Organizational Change Strategies
Force-Coercion Strategy
Changes are made through formal authority and/or the use of reward & punishment. Change is
obtained quickly but tends to be done because of fear of punishment or a desire for reward, the effects
are temporary. Suitable for use at the unfreezing stage, which is leaving old patterns and encouraging
the formation of new ones.
Rational Persuasion Strategy
Changes are made through knowledge, empirical data and rational arguments. Managers must use a
rational approach to provide great benefits compared to the previous pattern. Arguments can be
presented by agents of change, outside experts or through demonstrations. The changes that occur are
slower than the force-coercion strategy, but the results are more "durable" and internalized within the
individual.
Shared Power Strategy
Strategies that involve the participation of the parties involved to make changes according to the
values, needs and goals of the individual/group. Managers need reference power and skills to work
effectively with various parties. These changes take quite a long time, but these changes will be more
durable and internalized within each of them.
Based on the literature discussion above, the unified framework has been developed as below;
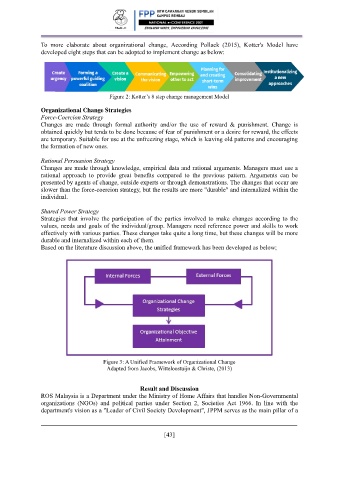
Figure 3: A Unified Framework of Organizational Change
Adapted from Jacobs, Witteloostuijn & Christe, (2013)
Result and Discussion
ROS Malaysia is a Department under the Ministry of Home Affairs that handles Non-Governmental
organizations (NGOs) and political parties under Section 2, Societies Act 1966. In line with the
department's vision as a "Leader of Civil Society Development", JPPM serves as the main pillar of a
[43]