Page 386 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 386
Carcinogenesis: Mechanisms and Models Chapter | 20 353
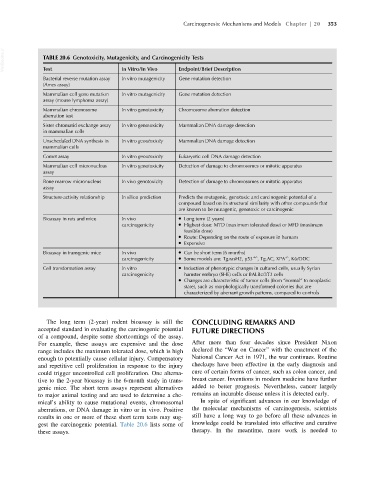
VetBooks.ir TABLE 20.6 Genotoxicity, Mutagenicity, and Carcinogenicity Tests
Test
In Vitro/In Vivo
Endpoint/Brief Description
Bacterial reverse mutation assay In vitro mutagenicity Gene mutation detection
(Ames assay)
Mammalian cell gene mutation In vitro mutagenicity Gene mutation detection
assay (mouse lymphoma assay)
Mammalian chromosome In vitro genotoxicity Chromosome aberration detection
aberration test
Sister chromatid exchange assay In vitro genotoxicity Mammalian DNA damage detection
in mammalian cells
Unscheduled DNA synthesis in In vitro genotoxicity Mammalian DNA damage detection
mammalian cells
Comet assay In vitro genotoxicity Eukaryotic cell DNA damage detection
Mammalian cell micronucleus In vitro genotoxicity Detection of damage to chromosomes or mitotic apparatus
assay
Bone marrow micronucleus In vivo genotoxicity Detection of damage to chromosomes or mitotic apparatus
assay
Structure-activity relationship In silico prediction Predicts the mutagenic, genotoxic and carcinogenic potential of a
compound based on its structural similarity with other compounds that
are known to be mutagenic, genotoxic or carcinogenic
Bioassay in rats and mice In vivo Long term (2 years)
carcinogenicity Highest dose: MTD (maximum tolerated dose) or MFD (maximum
feasible dose)
Route: Depending on the route of exposure in humans
Expensive
Bioassay in transgenic mice In vivo Can be short term (6 months)
-/-
carcinogenicity Some models are: Tg.rasH2, p53 1/- , Tg.AC, XPA , K6/ODC
Cell transformation assay In vitro Induction of phenotypic changes in cultured cells, usually Syrian
carcinogenicity hamster embryo (SHE) cells or BALBc/3T3 cells
Changes are characteristic of tumor cells (from “normal” to neoplastic
state), such as morphologically transformed colonies that are
characterized by aberrant growth patterns, compared to controls
The long term (2-year) rodent bioassay is still the CONCLUDING REMARKS AND
accepted standard in evaluating the carcinogenic potential FUTURE DIRECTIONS
of a compound, despite some shortcomings of the assay.
For example, these assays are expensive and the dose After more than four decades since President Nixon
range includes the maximum tolerated dose, which is high declared the “War on Cancer” with the enactment of the
enough to potentially cause cellular injury. Compensatory National Cancer Act in 1971, the war continues. Routine
and repetitive cell proliferation in response to the injury checkups have been effective in the early diagnosis and
could trigger uncontrolled cell proliferation. One alterna- cure of certain forms of cancer, such as colon cancer, and
tive to the 2-year bioassay is the 6-month study in trans- breast cancer. Inventions in modern medicine have further
genic mice. The short term assays represent alternatives added to better prognosis. Nevertheless, cancer largely
to major animal testing and are used to determine a che- remains an incurable disease unless it is detected early.
mical’s ability to cause mutational events, chromosomal In spite of significant advances in our knowledge of
aberrations, or DNA damage in vitro or in vivo. Positive the molecular mechanisms of carcinogenesis, scientists
results in one or more of these short term tests may sug- still have a long way to go before all these advances in
gest the carcinogenic potential. Table 20.6 lists some of knowledge could be translated into effective and curative
these assays. therapy. In the meantime, more work is needed to